Best Selling Products
Do You Really Understand Raster? Things Few People Tell You!
Nội dung
Raster is one of the most popular image formats in graphic design, but do you really understand it? This article will reveal little-known facts about Raster, helping you use this format most effectively in design and printing. Don't miss out on important information that you may not have heard before!
Graphic design is not just the art of arranging colors and images, but also the art of communicating messages through visual elements. When an image is used properly, it can tell a story, evoke emotions and create a deep impression on the viewer. However, each image is built from different formats, and choosing the right image format not only affects the quality of the image but also determines the effectiveness of the project's message. In that context, the two main image formats used in graphic design today are Raster and Vector. This article will help you better understand the two main image formats: Raster and Vector, from which you can choose and apply the most appropriate one for your design projects.
1. What is Raster?
Raster images, also known as pixel graphics, are images made up of thousands or even millions of pixels. Each pixel carries a specific color, and when they are arranged together in a certain matrix, they form the image we see on the screen or in print. The storage mechanism of raster formats depends on the location and color of each pixel, so the quality of the image is closely tied to the resolution.
.png)
For example, when you take a photo with a digital camera, the resulting image is a raster file with a fixed resolution. When you enlarge or print it at a larger size, if the original resolution is not high enough, the image will be blurry, pixelated and lose its inherent sharpness.
2. Raster file format
Common file formats for raster images include: JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, and TIFF.
2.1. JPEG
JPEG (short for Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a popular lossy image file format.
The JPG (or JPEG) file format is used to store and share digital images in many applications. One of the important advantages of the JPG format is its ability to compress images without losing too much image detail. This makes JPG a popular format for storing digital images on mobile devices and sharing them online.
When an image is saved in JPG format, it is compressed by reducing the amount of unnecessary data and removing some unimportant details. This compression process results in a reduction in file size and loss of some of the original image information. However, with the correct and appropriate level of compression, JPG still ensures good image quality and small file size.
.png)
The JPG format supports 24-bit color (16.7 million colors), allowing for a wide and varied color gamut. It also supports different levels of compression, allowing users to adjust the level of quality and file size as required.
The JPG format is popular in photography, web design, graphic design, printing, and many other applications involving digital image processing and sharing.
2.2. PNG
PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics, which is a popular image file format used to store and share digital images. It was developed as an improved version of the GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) format and supports lossy compression.
The main features of the PNG format include:
Color Depth Support: PNG supports 8-bit and 24-bit color depths, allowing images to be stored in 256 colors (8-bit) or 16.7 million colors (24-bit). This allows for accurate and varied color representation in images.
Transparency channel support: PNG allows the creation of images with a transparency channel, allowing parts of the image to show part of the background or layer behind when overlaid.
.png)
Lossy Compression: PNG uses lossy compression, which reduces file size without losing important image detail. This ensures good image quality while still having a smaller file size than other uncompressed or lossy formats.
Non-color data support: PNG can also store non-color data such as index data and marker data.
Lossless Flat Layers: PNG does not lose image detail during storage and compression. This is different from formats like JPEG, which may lose some image information to achieve a smaller file size.
The PNG format is popular in many fields, including graphic design, web design, computer graphics, and mobile applications. With its lossless data storage and transparency channel support, PNG is often used for charts, graphs, icons, screenshots, and many other applications.
2.3. GIF
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) is a popular animated image file format. GIF was originally developed by CompuServe in 1987 and has since become a popular format for sharing animated images on the web.
.png)
The main features of GIF images include:
GIF animation: allows to create animation by combining multiple images (frames) together. Each frame is displayed for a specified amount of time, creating a motion effect.
8-bit color support: GIF supports 8-bit color depth, allowing for the storage and display of up to 256 different colors. Each color is assigned a number from 0 to 255 in the color palette.
Lossless compression: GIFs use lossless compression, which reduces file size without losing image detail. However, this compression method is not effective for images with complex color shades or complex graphs.
Transparent channel support: GIF supports transparent channels, allowing the background of the animation to show through transparent areas.
Support for simple text and graphics: GIFs are suitable for simple animations such as charts, graphs, simple drawings, and compact animations.
.png)
GIF images are commonly used in web applications, websites, messages, charts, graphs, animated logos and other simple effects. The unique feature of GIF images is the ability to create compact and popular animations on the internet.
3. Resolution for raster images
The resolution of a raster image is the number of dots (pixels) in each unit of measurement of the image. Resolution is determined by two parameters: the width and height of the image, measured in pixels.
For example, if an image has a resolution of 1920×1080, this means that the image is 1920 pixels wide and 1080 pixels high. The total number of pixels in the image is 1920 x 1080 = 2,073,600 pixels.
The higher the resolution, meaning the more pixels there are, the more detailed and sharper the image will be. However, resolution also affects the file size of the image. Images with higher resolutions will have larger file sizes and take up more storage space.
.png)
Resolution is usually measured by the number of pixels across the width and height of the image, for example: 800×600, 1024×768, 1920×1080, etc. Resolution can also be measured by the number of pixels per unit of measurement, such as pixels per inch (PPI) or pixels per centimeter (PPCM), to determine the pixel density per unit length.
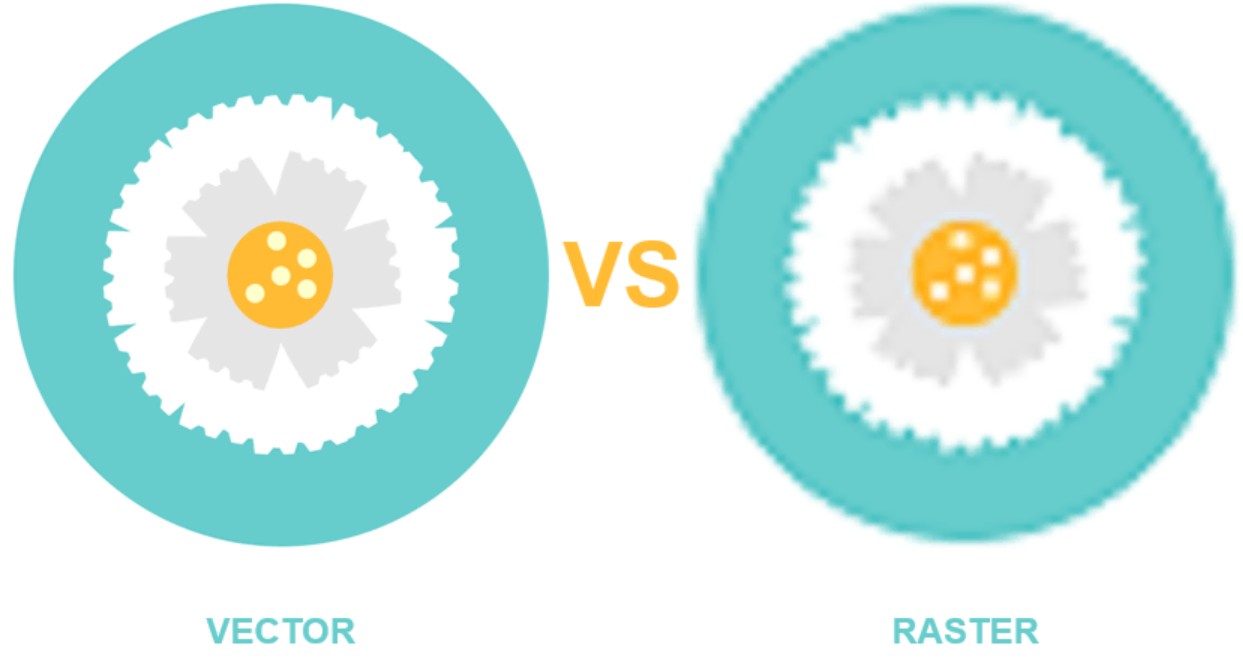
4. Distinguish between Vector and Raster
Raster images and vector images differ in structure, characteristics, scope of use, size and characteristics when enlarged or edited.
.png)
Raster
Vector
Structure
Raster images are made up of pixels in a rectangular grid.
Vector images are created using geometric drawing tools (lines, curves, shapes) and store data about objects and their properties.
Characteristic
Each pixel in a raster image stores information about its color and brightness.
Instead of storing individual pixels, vector images store geometric elements and their properties (position, color, size, …).
Scope
Raster images are suitable for displaying detailed, complex images such as photographs and natural images.
Vector images are suitable for creating simple images, charts, logos, line graphs, text, or any object that can be represented by geometric elements.
Size
Raster images have a fixed size and are limited by the number of pixels.
Vector images can be enlarged or reduced without losing the original image quality.
Feature
As a raster image is enlarged, the pixel size becomes more pronounced, reducing image quality.
Because they are pixel-independent, vector images can be edited, transformed, and recreated without affecting resolution.
5. Raster-based photo editor
There are many specialized software for processing and editing raster images. Here are some popular software in this field:
.png)
Adobe Photoshop: Is the leading raster image editing software and is widely used in the graphic design and photography industries. Photoshop provides powerful tools for editing, creating effects, retouching photos, and creating composite images.
GIMP: Is a free and open source raster image editing software. GIMP offers similar complex and professional tools to Photoshop and is a popular choice for those who do not want to use paid software.
Adobe Lightroom: This is a popular photo editing software dedicated to RAW and digital photography. Lightroom helps users organize, edit, and batch process photos efficiently.
Corel PaintShop Pro: Is a raster image editing software that provides tools for shaping, color correction, photo retouching and effects creation. It offers a user-friendly and reliable interface.
SaDesign hopes that the information shared in this article will help you gain a comprehensive view of two basic but equally important image formats in design. Choosing the right image format not only helps improve image quality but also optimizes the workflow, saving time and costs in the design process.












































