Best Selling Products
Learn What is Bitmap? How to distinguish bitmap images and vector images
Nội dung
- 1. Learn what Bitmap is?
- 1.1. Structure of Bitmap image
- 1.2. Popular bitmap image formats
- 1.3. Applications of bitmap images
- 2. How to distinguish Bitmap and Vector
- 2.1. About structure and operating principle
- 2.2. Image quality
- 2.3. File size
- 2.4. Practical application
- 3. Advantages and disadvantages of bitmap and vector
- 3.1. Advantages of bitmap images
- 3.2. Disadvantages of bitmap images
- 3.3. Advantages of vector images
- Conclusion
Learn what Bitmap is and the difference between Bitmap and Vector images. Detailed information is updated in the article, click to learn more!
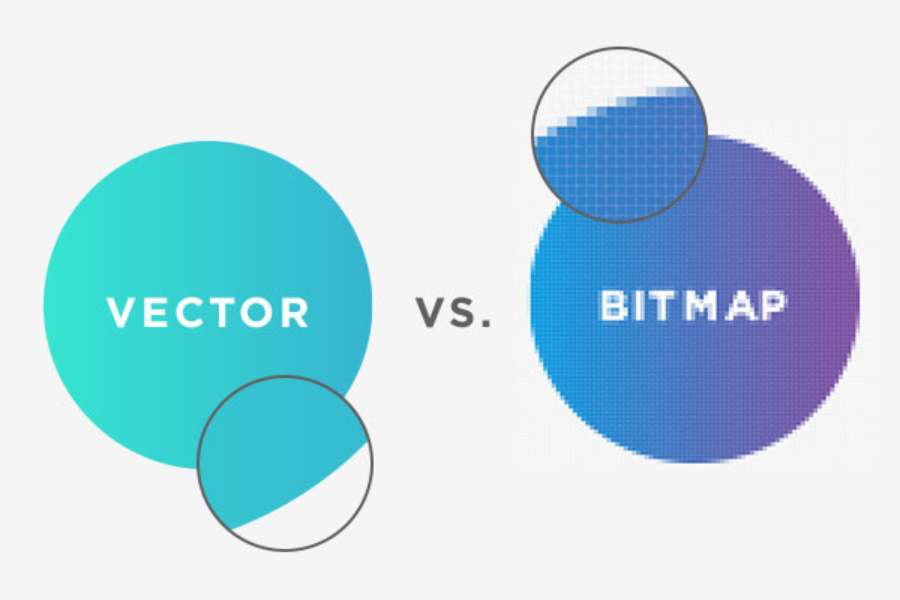
What is Bitmap and the difference between Bitmap and Vector images in the world of graphic design is extremely important. Although both serve the purpose of storing and displaying images, they have completely different technical characteristics. The article below SADESIDN will help you better understand these two types of images, and analyze their advantages and disadvantages.
1. Learn what Bitmap is?
Bitmap images (also known as raster images) are images made up of a collection of pixels. Each of these pixels has a unique color value, and when combined, they form the complete image we see on the screen.
1.1. Structure of Bitmap image
Each pixel in a bitmap can be described by a set of color values, usually expressed as binary code. The quality of a bitmap is determined by the number of pixels in the image, also known as the resolution. The higher the resolution, the sharper and more detailed the image. However, as a bitmap is enlarged, the pixels become more visible and result in pixelation, which reduces the image quality.

1.2. Popular bitmap image formats
Common bitmap image formats include:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): Popular format with high data compression, suitable for photos and images with rich colors.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): Supports transparency and does not lose image data like JPEG, commonly used in web design.
- GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): Used for animations, supports up to 256 colors.
- BMP (Bitmap Image File): Basic bitmap image format, rarely used in modern design.
1.3. Applications of bitmap images
Bitmap images are commonly used in areas such as:
- Photography: Photos taken from digital cameras, mobile phones.
- Graphic design: Advertising designs, book covers, posters, or illustrations.
- Web: Images on a website, including graphic elements and background images.
2. How to distinguish Bitmap and Vector
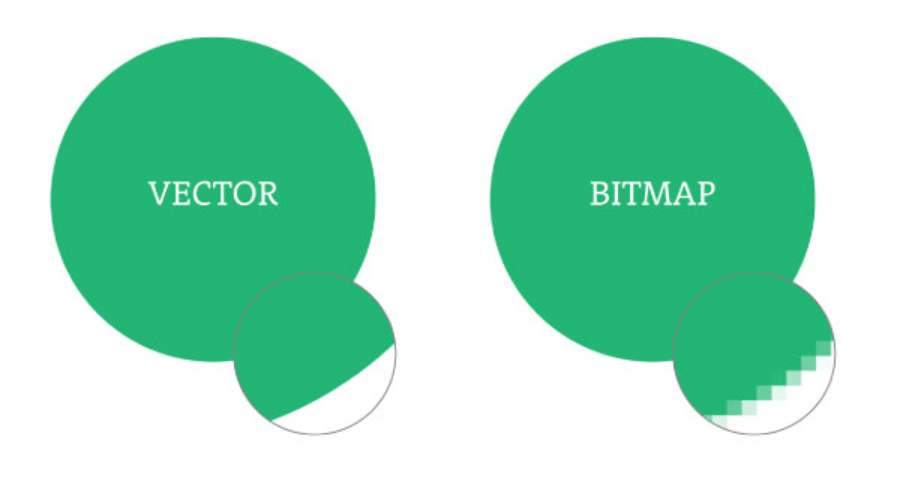
When comparing bitmap images with vector images, we can clearly see the difference between these two types of images in terms of structure, display method and application.
2.1. About structure and operating principle
- Bitmap: As mentioned, bitmap images are made up of pixels, each pixel having a specific color. These pixels will form the overall image when stacked on top of each other. Since bitmap images are a combination of pixels, when the image is enlarged, these pixels will be clearly visible, resulting in a pixelated image.
- Vector: Vector images, on the other hand, are constructed from mathematical objects such as lines, rectangles, curves, and other geometric shapes. These objects are described using mathematical equations instead of pixels. Therefore, vector images can be enlarged or reduced without losing quality.
2.2. Image quality
- Bitmap: The quality of a bitmap image is limited by the resolution of the image. As the resolution increases, the image becomes sharper, but if you zoom in too much, the quality will decrease significantly.
- Vector: Vector images are not affected by resolution. You can enlarge vector images without worrying about blurring or pixelation , because the objects in vector images are still perfectly reproduced thanks to mathematical equations.
2.3. File size
- Bitmap: Bitmap image files are often quite large in size, especially when the image is of high resolution. This makes it more difficult to store and load the image on devices or websites.
- Vector: Because vector images use only mathematical objects instead of pixels, vector image file sizes are typically smaller than bitmap images, even when the image has a lot of detail.
2.4. Practical application
- Bitmap: Often used for photographs, images with complex colors, or images that do not require much resizing.
- Vector: Suitable for designs that require high precision such as logos, maps, illustrations, and graphic elements that can be enlarged without losing quality.
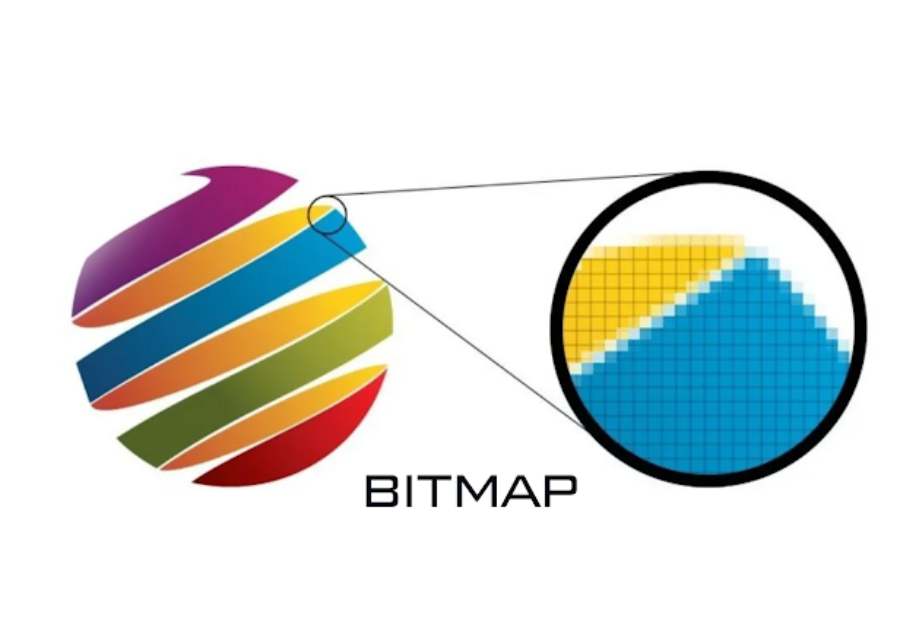
In short, the difference between bitmap and vector images lies not only in the structure but also in the practical use and application. Bitmap images with high resolution bring details and realism to photos, but have problems with file size and quality when enlarged. In contrast, vector images stand out with the ability to change size without limit while maintaining sharpness, suitable for graphic designs that require high flexibility.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of bitmap and vector
Each type of photo has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the purpose of use and user requirements.
3.1. Advantages of bitmap images
- High detail: Bitmap images show sharp image details, especially when used for photographs.
- Suitable for real-life photos: Due to their ability to show smooth color transitions, bitmaps are well suited for photographs, especially in the photography industry.
- Popular formats: Bitmap image formats like JPEG, PNG, GIF are very popular and easy to use on many different platforms.
3.2. Disadvantages of bitmap images
- Large file size: With high resolution, bitmap images can have very large file sizes, making them difficult to store and share.
- Loss of quality when zooming in: Zooming in on a bitmap image can result in pixelation, which reduces the sharpness of the image.
- Need specialized editing software: To edit bitmap images, users need software such as Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, or similar tools.
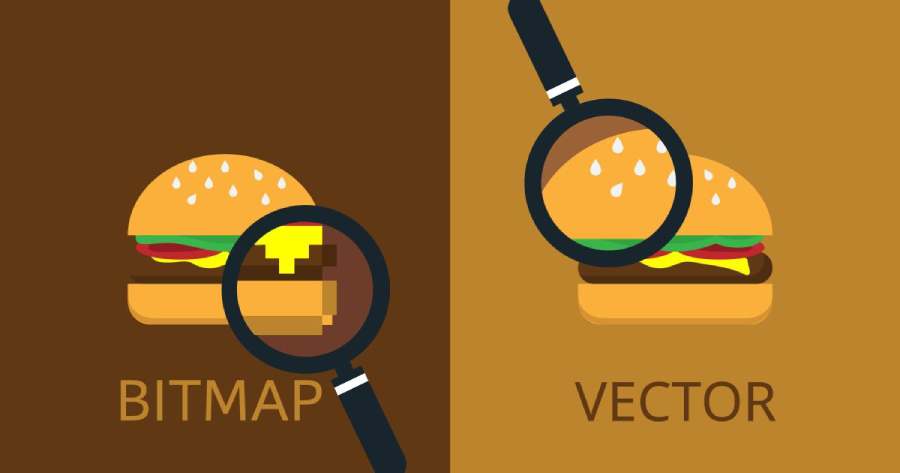
3.3. Advantages of vector images
- Lossless Scalability: One of the biggest advantages of vector images is the ability to scale up or down without losing image quality.
- Small file size: Thanks to the use of mathematical objects instead of pixels, vector images have compact file sizes, making them easy to store and upload to platforms.
- Easy to edit: With vector editing tools like Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, users can change the shape, color, and size of objects without affecting the overall quality.
3.4. Disadvantages of vector images
- Not suitable for photorealistic images: Vector images cannot reproduce the intricate details of photographic images like bitmap images. They are generally only suitable for graphic objects with clear shapes.
- Limitations on color and gradients: Although vector images can use colors and gradients, they cannot reproduce the smoothness of color like bitmap images.
Each type has different advantages and disadvantages. Depending on your needs and purposes, you can choose between bitmap and vector images to optimize work efficiency and ensure the quality of the final product.
Conclusion
Through the above article, SADESIGN has provided information on What is Bitmap? How to distinguish between bitmap images and vector images. Understanding the characteristics and how to distinguish between these two types of images will help you choose the format that suits each usage need. Don't forget to visit the SADESIGN Website to update the latest knowledge about graphic design right away!