Best Selling Products
The secret to creating impressive and effective products
Nội dung
- 1. Introduction to the importance of design optimization in printing
- 1.1. Color systems in printing
- 1.2. Image resolution
- 1.3. Choosing printing materials
- 1.4. Popular printing techniques
- 1.5. Notes on bleed and trim
- 2. Important factors in print design optimization
- 2.1. Choose the right color
- 2.2. Choose a font that is easy to read and appropriate .
- 2.3. Reasonable layout structure
- 2.4. Use high quality images
- 2.5. Professional layout
- 2.6. Use specialized design software
- 2.7. Check carefully before printing
- 2.8 Check File Size and Format
- 3. Factors affecting print quality
- 3.1. Printer quality
- 3.2. Ink quality
- 3.3. Printer's experience
- 3.4. Environmental conditions
- 3.5. Post-printing processing
- 4. Print design optimization process
- 4.1. Requirements and goals analysis
- 4.2. Prototyping and testing
- 4.3. Adjustment and completion
- 5. Benefits of optimizing design in printing
- 6. Conclusion
Explore print design optimization techniques to create impressive, professional, and effective products. Learn how to apply color, fonts, and design structure appropriately to each publication.

Optimizing design techniques in printing not only helps improve product quality but also brings maximum efficiency to advertising campaigns. In this article, sadesign will introduce important factors to optimize print design, from color selection, font to the overall structure of the printed product. If you are looking for a way to create beautiful, professional and effective printed products, do not miss the information below.
1. Introduction to the importance of design optimization in printing
In the printing industry, design plays a key role in determining the success of a product. A good design not only attracts attention but also helps to convey a strong and understandable message to the viewer. However, to create a perfect print design, it requires not only creativity but also adherence to optimization principles.
.jpg)
Optimizing design in print involves selecting elements such as color, layout, fonts, images, and balancing these elements to suit the intended use and target audience. This optimization not only saves costs but also ensures that the final product is of high quality and has maximum communication effectiveness.
1.1. Color systems in printing
RGB (Red, Green, Blue):
This is a color system that uses light to create color, often used for display devices such as computer screens, phones, and TVs.
Colors in the RGB system are very bright and vibrant, but cannot be reproduced accurately in printing.
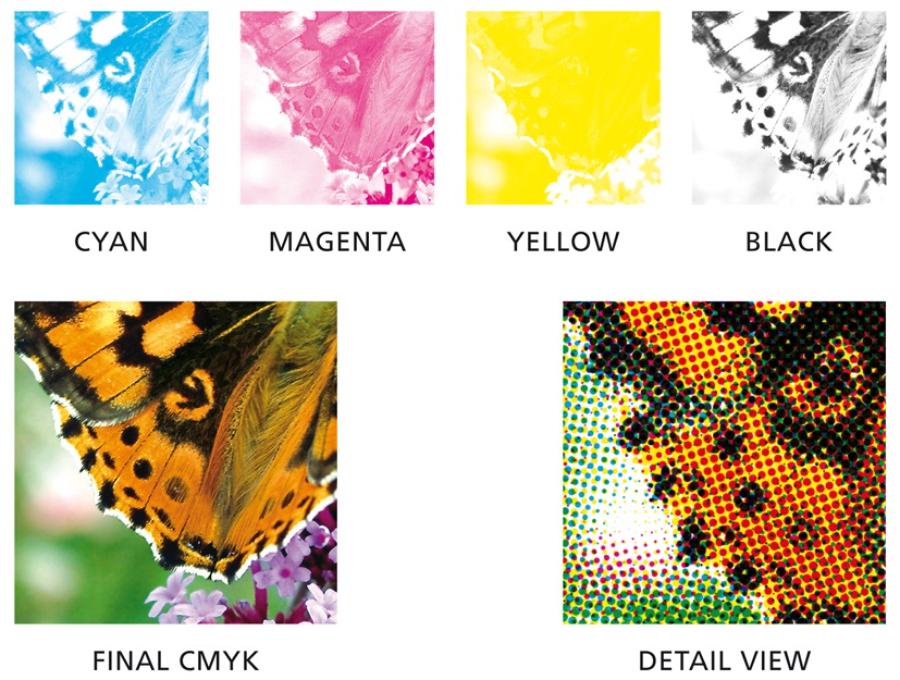
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black):
This is a color system that uses ink to create color, used in most printing processes.
Colors in the CMYK system are created by mixing primary ink colors.
It is important to convert your design from RGB to CMYK before printing to ensure colors are reproduced accurately.
Pantone:
This is a pre-mixed color system, used to ensure absolute color accuracy.
Each Pantone color has its own code, which helps printers mix ink in the correct proportions.
This color system is especially important when printing logos or designs that require high color accuracy.
1.2. Image resolution
DPI (Dots Per Inch):
This is a unit of measurement of pixels per inch.
The higher the resolution, the sharper and more detailed the image.
For printing, the minimum resolution is 300 DPI.
Using low resolution images will result in image fragmentation and blurring when printed.
1.3. Choosing printing materials
There are many different types of printing materials, each with its own characteristics and suitable for different types of printed products.
Printing paper:
Couche paper: Glossy, smooth paper, often used for printing magazines and brochures.
Bristol paper: Hard, smooth paper, often used for printing business cards and invitations.
Offset Paper: Offset paper, often used for printing books and newspapers.
Kraft paper: recycled paper, brown, is a popular trend.
Other materials:
Plastic: Often used for printing outdoor, waterproof products.
Fabric: Often used for printing clothing, flags, banners.
Metal: printing on metal materials used in printing signs or souvenirs.
1.4. Popular printing techniques
In offset:
This is the most popular printing technique, providing high print quality and suitable for large quantities.
The ink is pressed onto a rubber blanket, which is then pressed onto the paper.
Digital printing:
This is a fast printing technique and is suitable for small quantities.
Ink is sprayed directly onto the paper.
Screen printing:
This is a printing technique that can print on many different types of materials, giving outstanding colors.
The ink is forced through a mesh.
Flexo printing: is a direct printing method, using elastic printing plates. This type of printing is often used to print products in large quantities, especially packaging printing.
1.5. Notes on bleed and trim
Bleed:
This is the excess part outside the cutting line, helping to avoid revealing the white part of the paper when cutting.
Bleeds are typically 3mm to 5mm in size.
Trim line:
This is the final border of the product after printing.
Important design elements should be placed away from the cutting line to avoid being cut off.
2. Important factors in print design optimization
In the printing industry, design optimization plays an important role in ensuring the quality of the final product, while saving costs and improving production efficiency. An effective print design must not only meet aesthetic requirements but also comply with the technical requirements of the printing process. Below are important factors that designers and businesses need to keep in mind when optimizing print design.
.jpg)
2.1. Choose the right color
Color is a core element in print design, directly affecting the viewer's perception. When designing, it is necessary to use the CMYK color system instead of RGB, because CMYK is the standard color system used in printing. In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the contrast and saturation of the color to ensure consistency between the design on the screen and the actual printed product.
Colors have a great power in influencing the psychology of the viewer. Each color has its own meaning and emotion, for example, red represents strength and enthusiasm, while blue brings a feeling of relaxation and comfort. When optimizing print design, choosing the right color not only helps the product stand out but also helps in conveying the brand message.
When choosing colors, consider factors such as:
Brand recognition: Colors should match the brand image.
Aesthetics: Colors must be harmonious, easy to see and easy to combine with other elements such as fonts and images.
Printing efficiency: Colors must be compatible with printing technologies, ensuring that colors are accurately represented on the final product.
2.2. Choose a font that is easy to read and appropriate .
Fonts not only affect aesthetics but also the ability of the viewer to read. When choosing fonts, it is necessary to prioritize fonts that are clear, easy to read and suitable for the purpose of the product. At the same time, it is advisable to convert the text to vector format before sending the print file to avoid font errors.
Fonts are an essential element in print design, especially when your product needs to convey information clearly and easily understood. Fonts should be chosen to suit the design style and purpose of the product.
Criteria for choosing fonts include:
Easy to read: Avoid using overly complex or artistic fonts unless absolutely necessary.
Consistency: Avoid using too many fonts in one product. Stick to 1 to 2 main fonts to ensure consistency.
Match the message: The font should reflect the brand's personality and the message it wants to convey.
2.3. Reasonable layout structure
The design layout should be arranged in a harmonious, balanced way between visual elements, text and white space. A good layout not only creates attraction but also helps to convey the message clearly and effectively.
A good print design requires a good layout. Layout helps divide space, create balance, and direct the viewer to important parts of the design. To optimize the layout, the following factors should be considered:
Golden Ratio: This is a popular principle in design, which helps create harmony and comfort for the human eye.
White space: Even though the design is full of information, white space is still very important. It helps to keep the elements in the design from being crowded and creates comfort for the viewer.
Focus: Important elements that need to be highlighted, such as the brand name, advertising message or main product.
2.4. Use high quality images
Images in print design can be a deciding factor in the appeal of a product. A beautiful, high-quality photo will enhance the aesthetic value of the design and help viewers easily absorb the message. However, the use of images also requires careful consideration of resolution, quality, and relevance to the message.
Images used in print design need to be high resolution (minimum 300 DPI) to ensure print quality. Low resolution images will result in blurring, reducing the professionalism of the product.
Notes when choosing images for print design:
High resolution: Images must have a high enough resolution to avoid graininess when printed, ensuring sharpness and detail.
Relevant to the message: Images need to be relevant to the content and convey the right message you want to convey.
Consider color: Images need to blend with the overall color scheme of the design to create unity!
2.5. Professional layout
Use grids to create balanced and harmonious layouts.
Ensure spacing between design elements.
Pay attention to the viewer's reading order.
Use professional layout software such as Adobe InDesign or QuarkXPress.
Pay attention to fold lines, or crease lines, when designing products such as flyers, brochures, paper boxes...
2.6. Use specialized design software
Adobe Photoshop: Photo editing, effects creation, color manipulation.
Adobe Illustrator: Vector graphic design, logos, icons, illustrations. Create sharp, scalable images without pixelation.
Adobe InDesign: Layout of books, magazines, documents, brochures. Tight control over layout, fonts, images. CorelDraw: Vector design, advertising, printing, production. Friendly interface, easy to use.
2.7. Check carefully before printing
Check spelling, grammar, color, resolution.
Print a sample to check quality before printing in bulk.
Test design files on multiple devices.
Check the color system again, pay attention to convert the color system from RGB to CMYK.
Check the layers in the design file to avoid missing layers when printing.
Check carefully if the fonts have been converted to outlines.
Check the blending modes between design elements.
For printed products with UV coating, lamination, hot stamping... it is necessary to add a design layer for that processing part.
Check product dimensions again.
Check the die cut line for box-shaped products or products with special shapes.
2.8 Check File Size and Format
The size and format of your design file should match the requirements of your printer and the type of paper you are using. Common formats such as PDF, AI, or EPS are often preferred because they retain the quality of your images and text. Also, make sure that your design size includes the "bleed" to avoid cropping errors.
3. Factors affecting print quality
Print quality is influenced by many important factors, including the quality of printing materials such as paper and ink, the precision and modernity of printing equipment, as well as the technique and experience of the machine operator.
.jpg)
3.1. Printer quality
Modern, high-tech printers for better print quality.
Offset printing machines give higher print quality than digital printing machines.
Maintain and clean the printer regularly to ensure stable operation.
Check and calibrate your printer's colors regularly.
3.2. Ink quality
Use genuine, high quality ink.
Choose the right ink for the material you are printing on.
Poor quality ink can result in smudging, smearing, or incorrect color.
Good quality ink will keep its color longer.
3.3. Printer's experience
Experienced, highly skilled printers will produce quality printed products.
Printers can adjust the printer to achieve the best color and sharpness.
Communicate and work closely with printers to ensure best results.
The printer will be able to advise the designer on which type of printing material is best for the product.
3.4. Environmental conditions
Temperature and humidity affect print quality.
Printing paper may warp or shrink if stored in improper conditions.
Store printed materials in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
3.5. Post-printing processing
Laminating, hot stamping, embossing... create special effects for the product.
Choose the processing method suitable for the design and intended use.
Improper processing may damage the printed product.
Glossy lamination makes the color more vibrant, matte lamination makes the product more luxurious.
Foil stamping and hot stamping create highlights for the product.
Embossing and die-cutting create 3D effects for the product.
4. Print design optimization process
.jpg)
4.1. Requirements and goals analysis
Before starting to design, you need to clearly define the purpose of the printed product. You need to answer questions such as: What marketing campaign do you want this product to serve? Who is the target customer? Where and when will this product be used? From there, you will have clear parameters and requirements to carry out the appropriate design.
4.2. Prototyping and testing
Once you have defined your requirements, you can start creating design prototypes. This is an important step to check that elements such as colors, fonts, images, and layouts work well together. You will also need to experiment with different print formats to ensure that the design can be applied effectively to a variety of printed products.
4.3. Adjustment and completion
Once you have received feedback on your prototype, you need to tweak and refine your design to achieve maximum effectiveness. In this step, you need to pay attention to the small details, ensuring that every element of your design is perfect and in line with your original goals.
5. Benefits of optimizing design in printing
Optimizing print design offers many benefits to businesses and individuals, including:
Cost savings: By optimizing your design, you can minimize waste during the printing process, thereby saving on production costs.
Improve product quality: An optimal design will help print products have higher quality, increasing customer satisfaction.
Increase brand recognition: Beautiful and reasonable design helps your brand to be easily recognized and remembered by customers.
High communication effectiveness: An impressive and clear design helps convey the message strongly and easily understood.
6. Conclusion
Optimizing design in print not only helps you create beautiful products but also ensures effective communication and cost savings. Applying optimization techniques from color, font to layout and image will help improve product quality, while creating a strong impression on customers. Remember, a successful print design requires not only creativity but also adherence to basic principles to achieve maximum effectiveness.