Best Selling Products
Advanced Multimedia Applications for Effective UX/UI Design
Nội dung
- 1. What is Multimedia and Why is it Important in UX/UI?
- 1.1 Definition of Multimedia
- 1.2 The Importance of Multimedia in UX/UI
- 2. Popular Multimedia Forms Applied in UX/UI
- 2.1 Images
- 2.2 Audio
- 2.3 Video
- 2.4 Animation
- 2.5 Interactive Graphics
- 2.6 Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
- 3. Specific Applications of Multimedia in UX/UI Elements
- 3.1 Navigation
- 3.2 Content
- 3.3 Feedback and Interaction
- 3.4 Loading and Transitions
- 3.5 Onboarding and Tutorials
- 4. Benefits of Applying Multimedia in UX/UI
- 5. Challenges When Using Multimedia In UX/UI
- 6. Golden Rules When Applying Multimedia In UX/UI
- 7. New Multimedia Trends In UX/UI
- 9. Tools and Platforms Supporting Multimedia Applications
- 9.1 Interface design tools
- 9.2 Content Management Platform (CMS)
- 9.3 Multimedia storage and distribution platform
- 9.4 Multimedia creation and editing tools
- 10. Measuring the Effectiveness of Using Multimedia in UX/UI
- 11. The Future of Multimedia in UX/UI
- 13. Tips for UX/UI Designers When Working With Multimedia
- 14. Conclusion
Multimedia applications provide creative solutions, optimize UX/UI design, enhance user experience with effective combination of images, sounds and interactions.
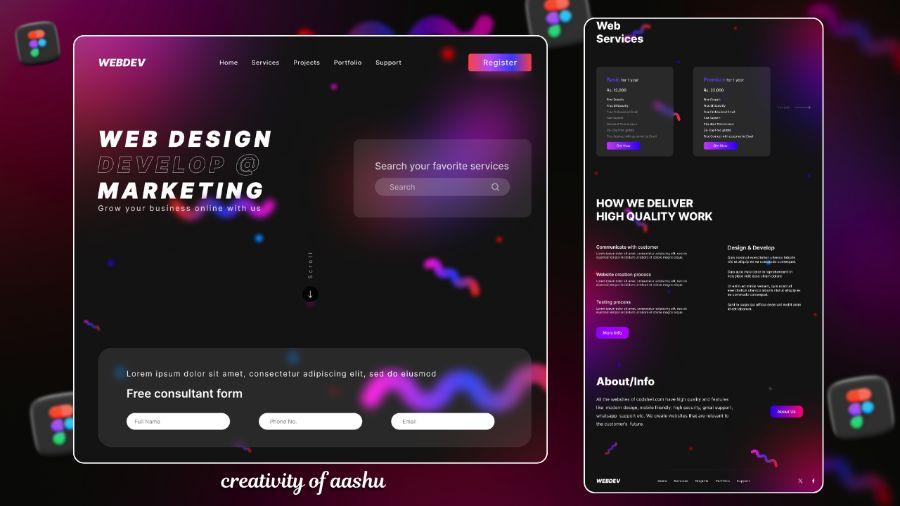
In the digital age, multimedia has become an indispensable part of creating engaging and effective digital products. Especially in the field of user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design, the smart application of multimedia can bring great benefits, from attracting attention to improving interactivity and conveying information. This article will delve into the diverse applications of multimedia in UX/UI, and analyze the benefits and challenges that come with it.
1. What is Multimedia and Why is it Important in UX/UI?
1.1 Definition of Multimedia
Multimedia is the combination of different forms of content such as text, images, audio, video, animation and other interactive elements. This integration creates a rich and multi-sensory experience for the user.
1.2 The Importance of Multimedia in UX/UI
Attention-Grabbing: Multimedia elements, especially animations and videos, are more likely to grab users' attention faster than plain text.
Effective information transmission: Multimedia can convey complex information in a more intuitive and understandable way, helping users grasp the content quickly.
Increased engagement: Interactive elements like 360-degree videos and customizable animations encourage users to explore and engage more deeply with the product.
Improve user experience: Using multimedia properly can create an interesting, engaging, and memorable user experience.
Increase aesthetics: Multimedia makes the interface more vivid, modern and professional.
Support diverse users: Multimedia can support users with different learning and information reception styles.
2. Popular Multimedia Forms Applied in UX/UI
2.1 Images
Application: Use high-quality images to illustrate content, create visual emphasis, convey emotion, and build brand recognition.
Examples: Product images on e-commerce sites, visual icons, website backgrounds, blog post illustrations.
2.2 Audio
Applications: Providing audio feedback for interactions (e.g. button clicks), creating atmosphere and emotion (e.g. background music), providing voice guidance or audio content (podcasts).
Examples: Success/failure notification sounds, website background music (optional), voice guidance in the tutorial app.
2.3 Video
Applications: Explain complex processes, introduce products or services, tell brand stories, provide visual instructions, create engaging advertising content.
For example: Product introduction videos on the homepage, feature tutorial videos, social media advertising videos.
2.4 Animation
Applications: Create smooth transitions, draw attention to important elements, explain abstract concepts, provide visual feedback for interactions.
For example: Page loading animations, mouse hover effects, process animations, micro-interactions.
2.5 Interactive Graphics
Application: Allows users to interact directly with data and images, explore information in their own way, creating personalized experiences.
For example: Interactive charts, zoomable and pannable maps, 3D models that can be rotated and drilled down.
2.6 Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Applications: Creating unique immersive and interactive experiences, especially in areas such as education, entertainment, e-commerce (e.g. 3D product preview in real space).
For example: Virtual museum tour app, virtual clothes try-on app, AR games.
3. Specific Applications of Multimedia in UX/UI Elements
.jpg)
3.1 Navigation
Images and icons: Use visual icons to represent navigation items, making them easy for users to recognize and navigate.
Animations: Create hover effects or smooth transitions when users interact with navigation items, providing visual feedback.
3.2 Content
Images and videos: Illustrate text, break up large blocks of information, and make content more engaging and understandable.
Audio and Voice: Provide content in audio format for users who are visually impaired or prefer listening to reading.
Interactive Graphics: Visualize complex data, allowing users to explore information in an interactive way.
3.3 Feedback and Interaction
Sound: Provide audio feedback for user actions (e.g. "click" when pressing a button, "ding" when receiving a new notification).
Animations: Use micro-interactions to provide visual feedback for small interactions (e.g. button click effects, loading effects).
3.4 Loading and Transitions
Page loading animation: Helps users feel the loading process is not too boring and provides information about progress.
Page Transition Effect: Create smooth transitions between pages or sections of an application, improving user experience.
3.5 Onboarding and Tutorials
Videos and animations: Explain product features and usage in a visual and easy-to-understand way.
Images and graphics: Guide users step-by-step through processes.
4. Benefits of Applying Multimedia in UX/UI
Increase user engagement and interaction: Multimedia creates a more engaging experience, encouraging users to spend more time on a website or app.
Improved information retention: Visual and multisensory content is often more memorable than plain text.
Enhanced accessibility: Multimedia can support users with different needs (e.g., visually impaired people can listen to audio content).
Building a strong brand: Consistent and creative use of multimedia helps create a unique and memorable brand image.
Increase conversion rates: Compelling multimedia content can convince users to take the desired action (e.g., purchase, sign up).
Reduce Bounce Rate: Engaging content keeps users on your site longer.
Increased shareability: Multimedia content is often easily shared on social media, increasing reach.
5. Challenges When Using Multimedia In UX/UI
Performance and loading speed: Large multimedia files can slow down page or application loading speed, affecting user experience. Optimize file size and use efficient loading techniques.
Compatibility: Ensure that multimedia formats are supported across a variety of devices and browsers.
Accessibility: Alternative options should be provided for users who cannot access multimedia content (e.g., alternative text for images, subtitles for videos).
Production costs: Creating high-quality multimedia content can be time-consuming and expensive.
Appropriateness: Indiscriminate use of multimedia can be distracting and reduce the effectiveness of information delivery. Ensure that the use of multimedia is appropriate to the purpose and audience.
Content Management: Managing and updating large amounts of multimedia content can become complex.
6. Golden Rules When Applying Multimedia In UX/UI
.jpg)
Relevance: Multimedia must serve a clear purpose and support the goals of the website or application.
Effectiveness: Multimedia must convey information effectively and easily understood.
Aesthetics: Multimedia should be of high quality and fit in with the overall design style.
Optimization: Multimedia must be optimized in size and format to ensure good performance.
Accessibility: Always provide alternative options for users who cannot access multimedia content.
Consistency: Use multimedia consistently across the entire interface.
User testing: Regularly test how users interact with multimedia content to make appropriate adjustments.
7. New Multimedia Trends In UX/UI
Interactive Video: Allows users to interact directly with the video (e.g., click on markers, answer questions).
360-degree images and videos: Provide a panoramic viewing experience and allow users to explore virtual environments.
Subtle micro-animations: Small animation effects that have a big impact on the feel of the interaction.
AI applications in multimedia content creation: Using artificial intelligence to create personalized and automated multimedia content.
Deeper integration of VR and AR: VR and AR applications in more areas, from online shopping to education and entertainment.
Visual Storytelling: Use multimedia to tell compelling stories and connect emotionally with users.
9. Tools and Platforms Supporting Multimedia Applications
Integrating multimedia into UX/UI design requires the support of specialized tools and platforms. Here are some common examples:
9.1 Interface design tools
Figma: Allows you to embed videos, GIFs, and create simple animation effects directly in your designs.
Sketch: Similar to Figma, supports plugins to integrate and preview multimedia elements.
Adobe XD: Provides powerful features for creating interactive prototypes with video, audio, and animation.
9.2 Content Management Platform (CMS)
WordPress: With a variety of plugins, WordPress makes it easy to embed images, videos, audio, and other multimedia into your website.
Drupal: Provides flexible and powerful multimedia management capabilities.
Contentful: A headless CMS that allows independent multimedia content management and distribution to multiple platforms.
9.3 Multimedia storage and distribution platform
YouTube/Vimeo: Popular video hosting platforms, easy to embed into websites or apps.
SoundCloud: Audio hosting and sharing platform.
Amazon S3/Google Cloud Storage: Cloud storage service that allows storage and distribution of large multimedia files.
CDN (Content Delivery Network): Helps deliver multimedia content quickly to users around the world.
9.4 Multimedia creation and editing tools
Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, After Effects, Premiere Pro, Audition): Professional toolset for creating and editing images, graphics, animation, video, and audio.
Canva: Easy-to-use online graphic design tool that offers a wide range of templates and multimedia resources.
Lottie: A library that allows exporting vector animations as compact JSON files, easily integrated into web and mobile applications.
10. Measuring the Effectiveness of Using Multimedia in UX/UI
To ensure that your multimedia implementation is truly beneficial, it is important to measure its effectiveness. Here are some metrics and methods you can use:
.jpg)
Time on Page: If users interact more with multimedia content, the time they spend on the page can increase.
Bounce Rate: Engaging multimedia content can reduce the rate at which users leave a site immediately after visiting it.
Conversion Rate: Track whether multimedia content positively impacts users taking the desired action (e.g., purchasing, signing up).
Engagement Rate: Measures the number of likes, comments, shares, or other interactions with multimedia content.
Video/audio completion: Track the percentage of users who watch the entire video or listen to an important audio segment.
Heatmaps and clickmaps: Use these tools to see how users interact with multimedia elements on the page.
User Feedback: Collect feedback directly from users through surveys, interviews, or other channels.
A/B testing: Testing different versions of a website or app with and without specific multimedia elements to compare performance.
11. The Future of Multimedia in UX/UI
Technological developments will continue to open up new possibilities for multimedia applications in UX/UI. Some notable future trends include:
AI-based personalized multimedia: Artificial intelligence will be used to create multimedia content tailored to each user's interests and behavior.
Deeper Immersive Experiences with Metaverse: The evolution of the metaverse will create rich 3D interactive spaces where multimedia plays a central role in creating immersive user experiences.
Seamless integration between the real and virtual worlds: AR and similar technologies will continue to blur the lines between the real and digital worlds, bringing unique multimedia experiences to everyday life.
Focus on performance and accessibility: New technologies will help optimize multimedia content delivery to ensure fast loading speeds and good accessibility for all users.
The rise of User-Generated Content (UGC) in the form of multimedia: Users will play an increasingly large role in creating and sharing multimedia content across platforms.
13. Tips for UX/UI Designers When Working With Multimedia
Always put the user first: Every decision about multimedia usage should be based on the needs and desires of the user.
Plan carefully: Clearly define the goals and messages you want to convey through multimedia.
Prioritize quality: Use high-quality multimedia content, in terms of images, sound and resolution.
Optimize performance: Make sure multimedia files are optimized so as not to slow down the user experience.
Ensure accessibility: Always provide alternative options for users who cannot access multimedia content.
Test and iterate: Monitor the effectiveness of multimedia use and make adjustments based on user feedback and data.
Trend Updates: Always be aware of new multimedia trends and how they can be applied in UX/UI.
Collaborate with experts: If needed, collaborate with graphic designers, filmmakers, and sound engineers to create high-quality multimedia content.
14. Conclusion
Mastering the art of multimedia in UX/UI design is a never-ending journey. With the rapid development of technology and changing user expectations, designers need to continuously learn and experiment to maximize the potential of multimedia. By combining creativity, user understanding and technical knowledge, we can create richer, more engaging and effective digital experiences than ever before. Multimedia is not just a decorative element but a powerful tool to enhance user experience and achieve business goals.












































