Best Selling Products
Bitmap: The Advanced Image Creation Technology Every Designer Needs to Know
Nội dung
- 1. Concept and operating mechanism of Bitmap
- 1.1. Bitmap Definition
- 1.2. How Bitmap works
- 1.3. Common Bitmap Formats
- 2. Advantages of Bitmap in practice
- 2.1. Outstanding image quality and detail
- 2.2. Easy to edit and process
- 2.3. Popular and strong support on many platforms
- 2.4. Practical applications in digital design and printing
- 3. Disadvantages of Bitmap in practice
- 3.1. Resolution limitations
- 3.2. Large file size and impact on page loading speed
- 3.3. Lack of flexibility when editing dimensions and changing structures
- 3.4. Limited application in modern design context
- 4. Difference between Bitmap and vector
- 4.1. Image format
- 4.2. Structure
- 4.3. Capacity
- 4.5. Bitmap applications in practice
- 5. How many ways are there to create Bitmap images?
Let’s explore Bitmap technology – an indispensable tool in graphic design. The article will present the technical aspects, advantages and disadvantages and why Bitmap has become the top choice in image production.
In the digital age, images play an extremely important role in conveying messages and building brands. In current image formats, Bitmap is always a familiar concept to designers and marketers. The following article will explore in detail about Bitmap when applied in practical design . At the same time, we will also compare Bitmap with other image technologies such as Vector to make appropriate creative decisions for each project. Let's find out with SaDesign !
First, let's delve into the concept and operating mechanism of Bitmap to get the most general overview.
1. Concept and operating mechanism of Bitmap
1.1. Bitmap Definition
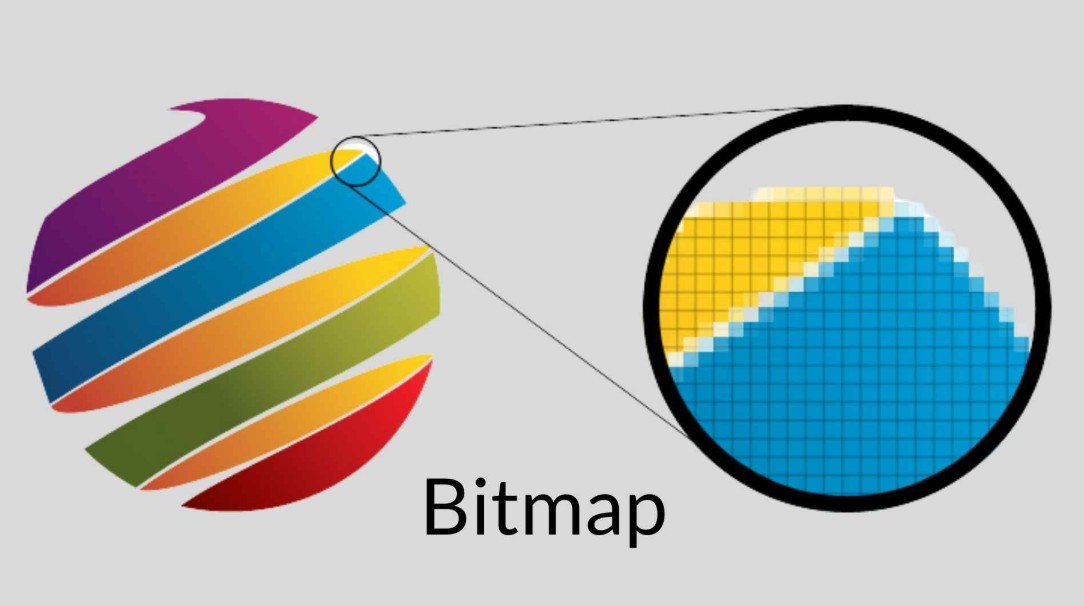
Bitmap is a digital image made up of a grid of pixels. Each pixel contains information about color, brightness, and contrast, contributing to the overall image. When you look at a Bitmap image, you see a tight combination of thousands, even millions of pixels arranged in an organized way to recreate the original image.
This concept helps users understand that, instead of storing images as mathematical formulas like vectors, Bitmap stores information directly for each pixel. This brings outstanding advantages in the ability to reproduce details, but at the same time also poses certain limitations.
.png)
1.2. How Bitmap works
When it comes to how Bitmaps work, the key is how the image data is stored and displayed. Specifically:
Pixel Grid: A Bitmap image is made up of pixels arranged in a grid of rows and columns. Each pixel has a fixed position, acting as a "piece" in the overall picture.
Color information: Each pixel contains color information, usually stored in RGB (Red, Green, Blue) format. Some formats also support an alpha channel to adjust the transparency of the pixel.
Resolution: This is the factor that determines the quality of the image. The higher the resolution, the more pixels there are, making the image sharper and more detailed. However, this also means that the image file size will increase.
Storage format: Bitmap has many different storage formats such as BMP, JPEG, PNG, GIF… Each format has its own advantages and disadvantages related to quality, file size and image processing capabilities.
.png)
Understanding how Bitmap works will help us easily compare it with other imaging technologies and know how to apply Bitmap in specific design projects.
1.3. Common Bitmap Formats
Each Bitmap format has its own unique characteristics, suitable for different purposes:
BMP (Bitmap Image File): This is the original Bitmap format, usually without data compression so the image quality is very high but the file size is also very large. BMP is often used in applications that need to ensure maximum quality.
JPEG: A popular format on the internet, JPEG uses lossy compression to reduce file size. However, the compression process can reduce image detail if not handled carefully.
PNG: Popular for its transparency support and lossless compression, PNG is suitable for web interface design and graphic products that need to retain details.
GIF: Particularly suitable for animated images with small file sizes, although only supporting up to 256 colors, GIF is still a popular choice for icons, memes or short advertisements.
.png)
Through this section, readers have had an overview of Bitmap and how it works. Next, we will move on to analyze the advantages of Bitmap in practice and why it is still popular despite certain limitations.
2. Advantages of Bitmap in practice
2.1. Outstanding image quality and detail
One of the biggest advantages of Bitmap is its ability to store complex image details. Each pixel in Bitmap carries specific color information, helping to reproduce the original image in the most realistic way. Especially when using high-resolution images, Bitmap can convey full color nuances, contrast and subtle details, which other formats cannot match.
2.2. Easy to edit and process
Another advantage of Bitmap is the ability to edit pixel by pixel, giving designers complete control over the image processing process. Software such as Adobe Photoshop, GIMP or CorelDRAW all support manipulation of Bitmap images well. This allows users to perform operations such as color correction, removing defects, creating special effects or even changing the image layout flexibly.
When working with Bitmaps, designers can easily magnify images to work on small details, thereby creating unique and personal effects for design products. This flexibility is one of the reasons why Bitmaps are popular in creative projects.
.png)
2.3. Popular and strong support on many platforms
Not only does Bitmap offer quality and editing capabilities, it is also widely supported on most platforms and devices. From desktops, mobile phones to professional printing devices, Bitmap is always the preferred format. Thanks to its high compatibility, Bitmap helps designers easily share, store and release products without too much trouble with formatting.
Furthermore, the popularity of Bitmap also means that there are many tools, plugins and support guides from the design community, helping users quickly get acquainted and apply them to their work effectively.
2.4. Practical applications in digital design and printing
In fact, Bitmap is widely used in many different design fields. Specifically:
Web design: Bitmaps in JPEG or PNG format are popular choices for displaying images on websites, from advertising banners to product photos.
Printing: With its ability to store high detail, Bitmap is the ideal choice for high-quality printing projects such as flyers, catalogs, brochures or magazine publications.
.png)
User Interface (UI) Design: Bitmaps help designers create interface elements with sharp details, supporting good user experience on mobile and web applications.
Digital Advertising: To create vivid and engaging images, Bitmaps are commonly used in online advertising and digital media campaigns.
The above advantages show that Bitmap is not only a traditional image format but also an effective tool in modern design projects. However, no technology is perfect, and Bitmap also faces some limitations when applied in certain cases.
3. Disadvantages of Bitmap in practice
3.1. Resolution limitations
One of the fundamental disadvantages of Bitmap is its dependence on the original resolution. Since Bitmaps are made up of fixed pixels, when you enlarge an image beyond its original resolution, the pixels will be stretched, resulting in a “blurry” or “pixelated” effect (obvious blocks of pixels), reducing the image quality.
This is especially important for projects that require large screen displays or require images to be enlarged without losing detail. This requires designers to carefully consider the initial resolution selection, thereby limiting errors during processing and publishing the product.
.png)
3.2. Large file size and impact on page loading speed
Another limitation of Bitmaps is that the file size can be very large, especially when using high resolution images. Each pixel in a Bitmap contains individual color information, which requires a significant amount of storage space. This causes a number of practical problems, such as:
Website Loading Speed: When using large Bitmap images for websites, page loading speed can be severely affected, especially on mobile devices or under bandwidth-limited conditions.
Storage and Management: Storing large amounts of Bitmap images also poses challenges for businesses in terms of data storage and resource management.
To overcome this problem, designers need to apply image optimization techniques such as compression and choose the right format to balance quality and file size.
3.3. Lack of flexibility when editing dimensions and changing structures
Compared to vector images, Bitmaps are more difficult to resize without losing quality. When resizing or performing complex editing operations, Bitmaps can lose their original sharpness, which can negatively affect the final product.
.png)
Additionally, changing a small part of a Bitmap image also requires careful editing to avoid confusing the viewer, especially for projects that require high precision such as product design or high-quality prints.
3.4. Limited application in modern design context
In the modern era of responsive design and diverse screen sizes, the use of Bitmaps needs to be carefully considered. Bitmap images, if not properly optimized, can have difficulty displaying on devices with different resolutions.
Particularly when designing user interfaces for mobile devices, the flexibility and scalability that vector formats offer is often preferred. Therefore, while Bitmap has many advantages in terms of detail and quality, when compared to other technologies, it has limitations that need to be taken into account to ensure optimal design performance.
4. Difference between Bitmap and vector
4.1. Image format
Due to the nature of the two images, they have different formats. With bitmap files, the higher the pixel density, the sharper the image. Therefore, bitmap graphics are exported as images and usually have formats such as JPG, JPEG, GIF, etc.
.png)
In contrast to bitmaps, vector images are created using graphic design software such as Corel or AI. So vector formats are usually CDR, PSD, AI, EPS or PDF, these formats often come with design software.
4.2. Structure
Bitmap image quality depends a lot on resolution. Therefore, when increasing or decreasing the size, the image will also change in quality. Specifically, when you reduce the size of the image through software or resize command, it means you will throw away pixels. When increasing the size of a bitmap image, the software will calculate the surrounding color values to add new pixels.
Vector images are created from many objects that can scale independently, so vector images are independent of resolution. Therefore, whether you increase or decrease the size, the vector image will maintain the same resolution, ensuring that the resulting image is still sharp. Especially with vector images, vector objects can be stacked on top of other objects.
4.3. Capacity
For a bitmap image to be sharp, the density of the pixels must be thick and numerous, which makes the capacity of a bitmap image higher, while vector images are the opposite. Therefore, for websites with too many bitmap images, using vector images is the first choice to optimize capacity.
.png)
4.5. Bitmap applications in practice
Technological devices with display screens are all used by manufacturers with Bitmap technology to make the display clearer and sharper. Along with that, Bitmap technology creates an optical sensor that records images when the camera is turned on. Therefore, all captured images are bitmap images.
With the development of mobile devices, the need for image editing and cropping is increasing. Using Bitmap images will help you easily edit, change or add effects to images such as smoothing, color changing, shading, etc. At the same time, Bitmap images are also easy to display and share, so they are used by many people to share with everyone.
Finally, bitmaps are ideal for creating realistic detailed images because each pixel stores a lot of data, and the range of colors displayed is also wider. Thanks to that, users can easily create a colorful, vivid image thanks to the ability to intelligently edit each color patch of the bitmap.
.png)
5. How many ways are there to create Bitmap images?
To create Bitmap images, we have 2 ways: taking photos and creating them with supporting software. But most of the Bitmap images today are created by taking photos, only a few are created with software by designers.
Photography can be done with phones, tablets, digital cameras and every day there are still many people diligently taking and producing new Bitmap photos. With the ease of editing, the number of Bitmap photos is increasing rapidly.
Compared to the total number of Bitmap images created, only a small number of images are created using editing and design software. All activities such as exporting vector image files to bitmaps or extracting images from videos are Bitmap image creation tasks. The most popular Bitmap image editing and creation software today is Photoshop.
The above article not only provides theoretical information about Bitmap but also detailed instructions on the steps of application and optimization when used in real design projects. Thereby, you can grasp the entire process from format selection, image processing to ensuring display quality on many devices.












































