Best Selling Products
Golden Ratio in Design: Concepts and Outstanding Applications
Nội dung
- 1. What is the golden ratio?
- 1.1 How the Fibonacci sequence is formed and its relationship with the golden ratio
- 1.2 The significance of the golden ratio in nature and art history
- 1.3 Why is the golden ratio considered the "ratio of nature"?
- 2. Why is the golden ratio so attractive?
- 3. Applying the golden ratio in graphic design
- 3.1 Image layout and composition
- 3.2 Logo design
- 3.3 Typographic design
- 4. The Golden Ratio in Web Design and UX/UI: Great User Experience
- 5. Unexpected Application: The Golden Ratio In Interior Design and Architecture
- 6. The Golden Ratio in Photography and Cinema: The "Perfect" Perspective
- 7. The Golden Ratio in Product Design: Functional and Emotional Beauty
- 8. Beyond Math: Design Thinking Based on the Golden Ratio
- 9. Conclusion
The golden ratio is a visual principle used in a wide range of creative fields. Let's explore the "divine" application of the golden ratio that many designers are still exploiting to the fullest.
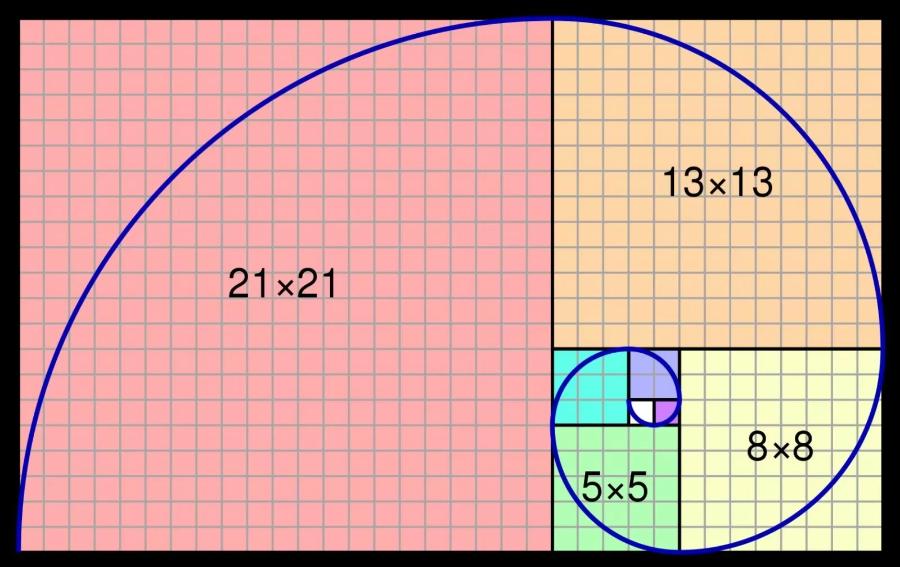
The golden ratio is not only a classical mathematical formula but also the foundation for creating harmony, balance and appeal in modern design. Used from ancient Greece to contemporary design works and products, the golden ratio proves its timeless influence in creating standard visual beauty. Let's find out more details with sadesign in the content below.
1. What is the golden ratio?
The Golden Ratio, also known as the Golden Ratio, is a special mathematical number that is approximately 1.618. When a line segment is divided into two parts such that the total length divided by the longer part is equal to the longer part divided by the shorter part, we have the golden ratio. The mathematical expression for the golden ratio is: (a + b)/a = a/b = φ (phi) ≈ 1.618
.jpg)
1.1 How the Fibonacci sequence is formed and its relationship with the golden ratio
The Fibonacci sequence is an infinite series of numbers in which each successive number is the sum of the two preceding numbers: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34,... When we take the ratio of two consecutive numbers in the Fibonacci sequence (the larger number divided by the smaller number) and move towards infinity, this ratio will approximate the golden ratio (1/1 = 1; 2/1 = 2; 3/2 = 1.5; 5/3 = 1.667; 8/5 = 1.6; 13/8 = 1.625,...). This relationship shows that the golden ratio is not just a dry number but also appears naturally in growth and development structures.
1.2 The significance of the golden ratio in nature and art history
The golden ratio and the Fibonacci sequence appear in an astonishing number of natural structures, from the arrangement of flower petals, nautilus shells, tree branches, to the spiral shapes of galaxies. In the history of art, many great works of architecture (the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Parthenon), famous paintings (Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa) and sculptures are said to follow or use the golden ratio to create visual balance and harmony.
1.3 Why is the golden ratio considered the "ratio of nature"?
The prevalence of the golden ratio and the Fibonacci sequence in nature suggests that there may be a deep connection between this ratio and the most efficient laws of growth and development. Structures that follow the golden ratio can achieve optimal balance, use space and energy efficiently, and are highly adaptable. Because of this widespread presence, the golden ratio has been called "nature's ratio."
2. Why is the golden ratio so attractive?
Human vision tends to love balance and harmony. The golden ratio creates a natural perfect composition, making the viewer feel comfortable and attracted. This is what makes the golden ratio a powerful tool in the hands of designers. The golden ratio is not imposed but flexible. It creates an ideal framework to guide the eye, control the emphasis and build a reasonable composition in a creative whole.
The Golden Ratio Creates Natural Balance and Harmony: When elements in a design follow the golden ratio, they create a natural sense of balance and harmony, similar to what we observe in the natural world. This balance is not forced, but rather pleasing and stable to the eye.
Visually stimulating and pleasing: Designs that use the golden ratio are often perceived as more aesthetically pleasing. It is hypothesized that the human brain is predisposed to favor these ratios, perhaps due to an inherent familiarity with them from nature. The golden ratio creates a smooth and attractive visual flow that draws and holds the viewer’s gaze.
Connection to spiral structures and growth in nature: The golden spiral, built on consecutive golden rectangles, appears a lot in nature (shells, sunflowers, tornadoes, etc.). Using curves and spiral layouts based on the golden ratio in design can create a sense of growth, movement and natural energy.
Potential applications in creating appeal and professionalism: By applying the golden ratio, designers can create products that are visually more appealing, professional, and trustworthy. The balance and harmony that the golden ratio brings can contribute to enhancing the perceived value of brands and products.
3. Applying the golden ratio in graphic design
In graphic design, the golden ratio can be applied to the arrangement of elements, including images, text, space, and size, to create a harmonious and professional whole.
.jpg)
3.1 Image layout and composition
In poster, banner, media publication or digital interface design, the golden ratio is often used to arrange the position of elements such as text, images, and icons. When the components follow the golden ratio rule, the viewer will feel neat, coherent and intuitive.
In user interface (UI) design, the golden ratio can be used to divide space in a visually appealing way. For example, the width of the main content column can be set to the golden ratio relative to the sidebar, creating visual balance and drawing the user’s attention to important content. Using a grid system based on the golden ratio also helps to organize elements on the page in a logical and easy-to-follow manner.
3.2 Logo design
Many famous brands such as Apple, Twitter and Pepsi have applied the golden ratio to their logo designs. Thanks to this ratio, the logo has the ability to maintain balance and consistency when zooming in, zooming out or switching display platforms.
The golden ratio can be used to create logos that are balanced, harmonious, and easily recognizable. Basic shapes such as circles, squares, and rectangles can be adjusted to the golden ratio to achieve aesthetic beauty. Many famous logos in the world are said to have the golden ratio embedded in their structure, such as the Apple logo, Twitter (the bird icon), and National Geographic. Applying the golden ratio not only makes a logo beautiful, but also gives a sense of stability and professionalism to the brand.
3.3 Typographic design
The golden ratio helps designers choose font size, line spacing, letter height, etc. to create harmony and ease of reading. When the letters follow a certain ratio system, the layout will become uniform and professional.
In typography, the golden ratio can be used to determine letter height and width, as well as kerning and leading. Some typographers believe that following the golden ratio can create typefaces that are naturally beautiful and easy to read.
4. The Golden Ratio in Web Design and UX/UI: Great User Experience
Building a grid system based on the golden ratio: Creating a grid system based on the golden ratio is a powerful way to ensure consistency and balance in web and app design. By dividing the width of the screen according to the golden ratio (e.g. 61.8% for the main column and 38.2% for the sidebar), designers can create a harmonious and easy-to-navigate page structure.
Content and image layout: The placement of content blocks, images, and other multimedia elements can be determined based on golden points or golden spirals. Placing important elements at these points can effectively attract users' attention.
Button and interactive element design: The size and placement of buttons, icons, and other interactive elements can be designed using the golden ratio to create balance and intuitiveness. A button that is sized in golden proportion to surrounding elements can look natural and be easily recognized by users.
Golden Ratio White Space: The strategic use of white space is crucial in UX/UI design. Applying the golden ratio to determine spacing between elements, page margins, and white space around objects can significantly improve the aesthetics and readability of an interface.
Optimize the mobile experience: Although space on mobile devices is limited, the golden ratio principle can still be applied flexibly to create balanced and easy-to-use layouts on small screens. Prioritizing important content according to the golden ratio can help users focus on key information.
5. Unexpected Application: The Golden Ratio In Interior Design and Architecture
.jpg)
Space and furniture layout: In interior design, the golden ratio can be used to determine the position of large furniture (sofas, beds, cabinets) in relation to the overall size of the room. Arranging according to this ratio can create a balanced, harmonious space that brings a sense of comfort.
Facade design and proportions of architectural details: Many classical and modern architectural works are said to follow the golden ratio in the design of the facade, the ratio between height and width, as well as the proportions between details such as doors, windows and pillars. The application of the golden ratio brings a balanced, elegant and timeless beauty to the works.
Choosing the size of doors, windows and decorative elements: The size of doors, windows and decorative elements such as pictures and mirrors can also be chosen based on the golden ratio compared to the size of the wall and surrounding space. This helps create proportional harmony and enhances the aesthetics of the space.
Creating Golden Ratio in Landscapes and Green Spaces: In landscape design, the golden ratio can be used to arrange elements such as walkways, planting areas, water bodies and small architectural structures. Following this ratio can create a natural, harmonious and relaxing space.
6. The Golden Ratio in Photography and Cinema: The "Perfect" Perspective
The Rule of Thirds and its Relationship to the Golden Ratio: The Rule of Thirds, a fundamental compositional principle in photography and cinema, is closely related to the golden ratio. By dividing the frame into nine equal parts using two horizontal and two vertical lines, the intersection points of these lines (the golden points) are considered powerful locations for placing important objects, attracting the viewer's attention.
Golden Points and How to Attract the Viewer's Attention: Placing main subjects or important elements in the frame at golden points can create a more balanced, attractive and natural composition than placing them in the center.
Using the Golden Spiral to Lead the Eye: The golden spiral can be used as a compositional tool to lead the viewer’s eye through important elements in the frame in a smooth and natural way. Placing focal points of the photo or shot along this spiral can create a dynamic and engaging composition.
Apply the golden ratio in choosing aspect ratios: Some common aspect ratios in photography and cinema (e.g. 16:9) are close to the golden ratio. Choosing the right aspect ratio can affect the sense of balance and harmony in an image or video.
7. The Golden Ratio in Product Design: Functional and Emotional Beauty
.jpg)
Product shape and size design: The golden ratio can be used to determine the overall shape and relative sizes of parts in a product. Adhering to this ratio can create products that have a balanced, harmonious appearance and a comfortable feel.
Arranging components and interfaces on technology products: In user interface design on electronic devices (phones, tablets, computers), the golden ratio can be used to arrange buttons, displays and other interactive elements in an intuitive and easy-to-use way.
Application in product packaging design: The golden ratio can be used to create attractive packaging designs that attract the attention of buyers. Arranging logos, product images and information in the golden ratio can create a balanced and professional design.
Balance between function and beauty thanks to the golden ratio: Applying the golden ratio in product design not only brings aesthetic beauty but can also contribute to optimizing function and user experience by creating balance and harmony between elements.
8. Beyond Math: Design Thinking Based on the Golden Ratio
The Golden Ratio is not a hard and fast formula, but a guide: It is important to remember that the Golden Ratio is not an absolute rule, but a tool and a source of inspiration. Designers do not have to follow this ratio mechanically, but should use it as a guide to create balance and harmony.
Flexibility and creativity in applying the golden ratio in practice: Applying the golden ratio requires flexibility and creativity on the part of the designer. Sometimes, slight adjustments to the ratios to suit the specific context of the project are necessary.
Combining the Golden Ratio with Other Design Principles (Balance, Contrast, Rhythm): The Golden Ratio should be considered in conjunction with other design principles such as balance, contrast, rhythm, and emphasis. Combining these principles harmoniously will create effective and beautiful designs.
Learn to “feel” the golden ratio through practice and observation: With time and experience, designers can develop a “feel” for the golden ratio, allowing them to apply it intuitively without needing precise measurements. Observing successful examples and practicing regularly are key to developing this ability.
9. Conclusion
The golden ratio is not a magic wand that will turn you into a talented designer overnight. But understanding and applying this principle well will help you build a solid design foundation, making more accurate layout and aesthetic choices. Think of the golden ratio as a companion, silently supporting you on your journey to creating attractive and professional design products.