Best Selling Products
Explore In Detail Core Terms In The UI/UX Field (P2)
Nội dung
- 1. UI vs UX: The Basic Difference
- 2. Wireframe - Interface Frame (Wireframe)
- 3. Prototype - Test Model (Prototype)
- 4. Interaction Design (IxD) - Interaction Design
- 5. User Flow - User Process
- 6. Responsive Design - Responsive Design
- 7. Usability - Ease of Use
- 8. Heuristic Evaluation - Evaluation Based on Rules of Thumb
- 9. Affordance - Interoperability
- 10. Microinteractions - Small Interactions
- 11. Visual Hierarchy - Visual Hierarchy
- 12. Conclusion
Learn more about important UI/UX terms and how they affect user experience. This article provides an in-depth understanding of important elements in user interface design.

In part 2 of our series “Decoding Basic UI/UX Terms,” we’ll continue exploring key terms that will help you better understand user interface and user experience design. Understanding these terms will not only enhance your design skills, but also improve the effectiveness of your digital products.
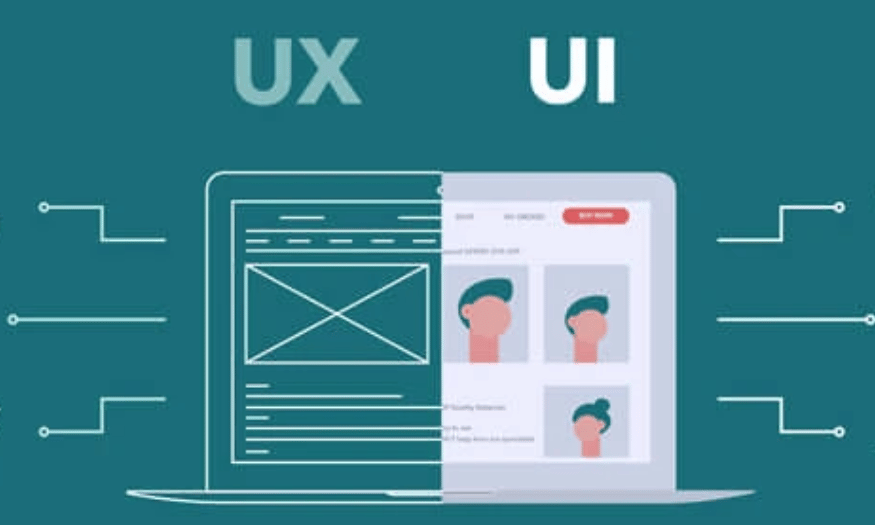
1. UI vs UX: The Basic Difference
Before we get into the specifics, it is important to understand the difference between UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience). UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) are two important concepts in the field of digital product design, but they have distinct differences in their roles and purposes. Although they are often used interchangeably, they actually have different roles and purposes in design.
.jpg)
UI refers to everything the user can see and interact with on the interface, including buttons, menu bars, icons, colors, fonts, and any other visual elements.
UX is the overall experience a user has when using a product or service. It includes the feel, ease of use, smoothness of features, and the feeling the user gets when interacting with the product.
2. Wireframe - Interface Frame (Wireframe)
Wireframes, also known as interface frameworks, are an important tool in the user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design process. They are rough sketches that help define the structure, layout, and key components of a digital product such as a website or app. Wireframes do not focus on aesthetics, but rather on defining how content is arranged, the flow of interactions, and basic functionality. Using wireframes helps design and development teams get an overview, easily exchange ideas, and ensure that the final product meets the needs of users.
A wireframe is a rough sketch of a website or app that defines the basic structure of a website or app. It is the first step in the design process, giving the development and design team an overview of how the elements on the page will be laid out.
Wireframes are typically minimal in detail and color, focusing on basic elements like navigation, content, images, and buttons. The main goal is to help teams quickly agree on the idea and structure of the page.
3. Prototype - Test Model (Prototype)
A prototype, also known as a test model, is a trial version of a product or system intended to be tested, evaluated, and refined before it is put into official use. This is an important step in the development process, helping businesses or engineering teams identify potential problems, improve features, and ensure that the product meets actual requirements. Creating a prototype not only saves time and costs during the implementation process, but also improves the quality and efficiency of the final product.
.jpg)
It provides a clearer representation of the functionality, interactions, and feel of the actual product. It is an important tool for designers and developers to test, experiment, and refine before the final product is released.
Prototypes can often be "clickable", meaning users can interact with elements on the interface to see how the functionality works in practice.
4. Interaction Design (IxD) - Interaction Design
Interaction Design (IxD) is an important field in user experience design, focusing on creating systems, interfaces and products that meet users' needs through effective interactions. The goal of interaction design is not only to ensure aesthetics but also to optimize the convenience, intuitiveness and usability of the product. By studying user behavior, combined with design principles and technology, IxD plays a key role in building seamless experiences that help users achieve their goals easily and with satisfaction.
Interaction Design (IxD) is the process of designing how users interact with a system. This involves not only the user interface but also how the elements within the interface respond to the user, such as the effects of button presses, page transitions, notifications, or feedback when performing an action.
A good interaction design not only creates a beautiful interface but also ensures that the user feels comfortable and at ease throughout the usage process.
5. User Flow - User Process
User Flow is an important part of user experience design, helping to ensure that users can easily complete their goals on a platform or application. This process involves identifying and optimizing the steps that users will take, from the beginning of an interaction to achieving the desired outcome. An effective user flow not only improves user satisfaction but also contributes to business performance, reduces pain points, and enhances the competitiveness of the product in the market.
(1).jpg)
A User Flow describes the journey a user takes when interacting with a product. It is a diagram or chart that illustrates how a user moves through the different steps in an application or website, from when they start until they complete a specific goal (e.g., completing a purchase, signing up for an account, etc.).
Understanding user flows helps designers create streamlined interfaces, minimize redundant steps, and ensure that users can achieve their goals efficiently.
6. Responsive Design - Responsive Design
Responsive Design is a web design method that ensures that the interface of a website or application automatically adjusts to fit the screen size of the device the user is using, from desktop computers to mobile phones.
By using techniques such as flexible grids, flexible images, and media queries, responsive design allows a website to automatically adjust its size, layout, and functionality based on the screen size and resolution of the device. This not only improves user accessibility and engagement, but also contributes to improved SEO performance, enhancing the professionalism and competitiveness of businesses in today's digital environment.
Responsive design improves user experience and ensures your products are easily accessible across a variety of devices without sacrificing the aesthetics or functionality of the interface.
7. Usability - Ease of Use
Usability, also known as ease of use, is an important factor in UX. It refers to the ease with which a user can access and use a system, product or service. An easy-to-use product is one that requires little learning and allows users to perform their desired actions without any difficulty.
8. Heuristic Evaluation - Evaluation Based on Rules of Thumb
Heuristic Evaluation is a method of assessing the quality of an interface based on simple design rules, or "heuristics". Designers use this method to quickly and efficiently detect problems in interfaces and user experiences.
One of the popular sets of rules applied in heuristic evaluation is Jakob Nielsen's 10 principles, which help detect usability and accessibility issues.
9. Affordance - Interoperability
Affordance in interface design refers to the ability of an object on the screen to suggest to the user that it is a clickable object. For example, a button that changes color when hovered over suggests to the user that it is a clickable object.
.jpg)
Affordance makes it easy for users to understand how to interact with an interface without having to think too much about how it works.
10. Microinteractions - Small Interactions
Microinteractions are small, simple interactions that are incredibly important in improving the user experience. They can be small effects on button presses, status notifications, or even dynamic changes in menu items.
While these interactions may be small, they can make a big difference in user experience, resulting in a smoother and more enjoyable user experience.
11. Visual Hierarchy - Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy is a design principle that helps create a visual order of priority for elements on an interface, helping users easily identify and interact with the most important parts of the product.
Arranging elements logically by size, color, and position on the page makes it easier for users to focus on the necessary parts and makes the user experience more intuitive and efficient.
12. Conclusion
Mastering the basic UI/UX terminology is an important step to improve your ability to design and develop digital products. Each term contributes to building a product that is not only beautiful but also provides a great user experience. Continuing to explore and apply these terms will help you develop your design skills and optimize your products to bring the highest satisfaction to users.