Best Selling Products
What is Design Thinking? The Creative Key Every Designer Needs to Know!
Nội dung
- 1. What is Design Thinking?
- 2. Outstanding features of design thinking
- 2.1. Human-Centered
- 2.2. Creativity
- 2.3. Iterative
- 2.4. Empirical
- 2.5. Collaboration
- 3. Design Thinking Process
- 3.1. Phase 1: Understanding
- 3.2. Phase 2: Identification
- 3.3. Phase 3: Idea generation
- 3.4. Phase 4: Prototyping
- 3.5. Phase 5: Testing
- 4. Benefits and Practical Applications
- 4.1. Benefits
- 4.2. Application
Design Thinking is a human-centered, creative problem-solving process that focuses on understanding real user needs, generating innovative ideas, building prototypes, and continuously testing to find optimal solutions.
In a world that increasingly values creativity and innovation, design thinking is no longer a concept reserved for designers alone. Today, from technology companies and startups to education and healthcare – design thinking is increasingly becoming a strategic approach to solving problems and creating real value.
So what is design thinking , why is it important, and how can it be effectively applied in work and daily life? In this article, we will comprehensively explore the basic concepts and processes of design thinking, as well as practical applications to help you improve work performance, develop creative ideas, and improve user experience in a sustainable way.
1. What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a human-centered, creative problem-solving process that focuses on understanding real user needs, generating innovative ideas, building prototypes, and continuously testing to find optimal solutions. It is not simply about designing a product or service, but a way of thinking to solve complex challenges more effectively and creatively.
Have you ever wondered why some products or services work perfectly for you, while others disappoint? The secret may lie in the thinking behind their creation. Welcome to the world of design thinking – a creative and effective approach to problem solving, not just for designers, but for anyone who wants to make a difference.
Design thinking is not just an abstract concept but a practical process that is becoming increasingly popular in all areas, from business to education to social issues. With design thinking, you can turn complex challenges into opportunities for innovation, creating solutions that are not only useful but also meet the needs of users.
.png)
The biggest difference between design thinking and traditional problem-solving approaches is its human-centered nature. Instead of focusing on technical solutions or individual ideas, design thinking puts users and their needs first. It encourages us to dig deeper into understanding, explore underlying problems, and find the most suitable solutions. Unlike a linear approach, design thinking is an iterative process, allowing you to continuously improve and refine your solution based on real-world feedback.
As the world continues to change and problems become more complex, we need a new way of thinking to address these challenges. Design thinking not only helps us find creative solutions but also helps us create real value. With design thinking, you don’t just solve problems but also create products, services and experiences that bring satisfaction and happiness to users.
2. Outstanding features of design thinking
Design thinking is not a rigid process but a flexible way of thinking, based on the following core characteristics:
2.1. Human-Centered
This is the heart of design thinking. Rather than focusing on technical solutions or subjective ideas, design thinking puts the people who use the solution first.
The Importance of Understanding Users: To create truly effective solutions, we need to understand the needs, desires, and challenges that users face. This is not just about listening to what they say, but also observing, feeling, and empathizing with their experiences.
For example: Instead of designing a phone with a lot of complicated features, a design-thinking designer would focus on the real needs of the user, such as simplicity, ease of use, and the ability to connect with loved ones. They would find out what users really need, what features they use frequently, and what difficulties they encounter when using their phones. Based on that information, they would design a phone that truly meets the needs of the user, instead of just following the market trend.
.png)
2.2. Creativity
Design thinking encourages creativity and innovation, not being afraid to try new ideas, even those that seem “crazy”.
The Role of Creativity: Creativity is essential to finding unique and innovative solutions. Design thinking provides a safe environment for us to freely explore and experiment with different ideas, without fear of mistakes and failures.
Don't be afraid to experiment and push the boundaries: Design thinking encourages us to question the obvious, challenge old rules, and find new approaches.
2.3. Iterative
Iterative and continuous improvement process: After testing, we collect feedback, analyze the results, and continue to adjust and improve the solution until we achieve the best results.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Iteration makes design thinking more flexible, able to adapt to changes and new requirements during implementation.
2.4. Empirical
Design thinking encourages us to “get hands-on,” create prototypes, and test them to evaluate the feasibility of the solution.
The Role of Prototyping and Testing: Rather than just stopping at ideas, prototyping and testing helps us evaluate feasibility, identify potential problems, and collect real feedback from users.
Learn from mistakes and continuously improve: Mistakes and failures are an integral part of the design thinking process. It is important that we learn from these mistakes and continuously improve our solutions.
.png)
2.5. Collaboration
Design thinking is often done in teams, leveraging the diversity of knowledge and experience of members to come up with a comprehensive solution.
Benefits of teamwork: Working in teams helps us have different perspectives on the problem, take advantage of each member's knowledge and experience, thereby creating more creative and comprehensive solutions.
Diversity of perspectives and experiences: Design thinking encourages diversity, which helps us look at problems from different perspectives, avoiding biases and barriers in the thinking process.
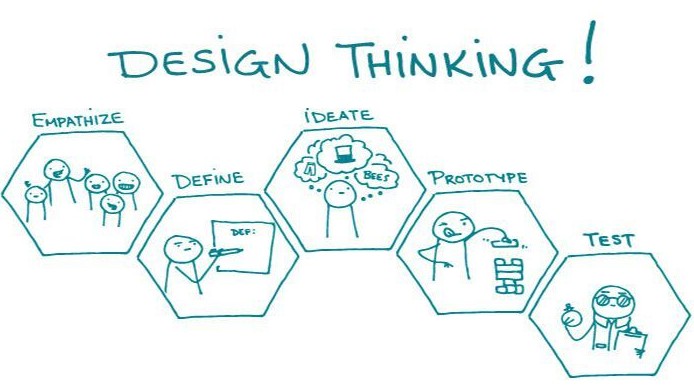
3. Design Thinking Process
Now that we have a clear understanding of the concept and characteristics of design thinking, let’s explore its actual process. Design thinking is usually carried out in 5 main stages, which are iterative and complementary to each other. This process not only helps us solve problems systematically but also encourages creativity and innovation in the working process.
Each stage has a specific goal and uses different methods, all aimed at the ultimate goal of finding solutions that best meet user needs.
3.1. Phase 1: Understanding
Objective: This first phase focuses on getting to know your users and their problems in depth. We need to put ourselves in their shoes and understand their needs, desires, and pain points. This is a crucial step to ensure that the solution we create is meaningful and meets real needs.
.png)
Commonly used methods:
Observation: Observe users' behaviors, habits, and how they interact with their surroundings.
Interviews: Talk directly with users to gather insights about their experiences and perspectives.
Research: Examine documents, data, and reports relevant to the problem.
3.2. Phase 2: Identification
Objective: After gathering enough information from the Understand stage, the Define stage focuses on synthesizing and analyzing the information to clearly define the problem to be solved. We need to define the problem in a specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) way.
How to define the problem clearly and measurably:
Specific: Define the problem clearly, not generally.
Measurable: Provide criteria to measure the success of the solution.
Achievable: Ensures that the solution is feasible under current conditions.
Relevant: Make sure the problem is relevant to user needs and overall goals.
Time-bound: Set a specific time frame for implementing the solution.
.png)
3.3. Phase 3: Idea generation
Objective: This stage focuses on generating as many ideas as possible to solve the identified problem. We need to create an environment that encourages creativity, and is not afraid of “crazy” or different ideas.
Methods:
Brainstorming: The group comes up with ideas together, without criticism or evaluation.
Reverse Brainstorming: Think about the worst things that could happen, then find ways to prevent them.
Sketching: Draw out ideas quickly and visually.
3.4. Phase 4: Prototyping
Objective: This phase focuses on turning the best ideas into simple prototypes for testing. Prototypes can be sketches, models, or any form that helps us visualize and test the feasibility of the solution.
Different prototype forms:
Drawing: Sketch out ideas on paper.
Model: Build a 3D model of the product.
Scenario: Write out a detailed scenario of how the user interacts with the solution.
Mock App: Create a simple version of your app.
.png)
3.5. Phase 5: Testing
Objective: This final phase focuses on getting the prototype out to users to test and collect feedback. This feedback will help us evaluate the effectiveness of the solution and identify areas for improvement.
How to collect and analyze feedback:
Observation: Observe how users interact with the prototype.
Interviews: Ask users about their experiences and opinions about the solution.
Surveys: Use surveys to collect feedback from multiple users.
4. Benefits and Practical Applications
Now that you have a solid grasp of the concepts and processes, you may be wondering, “What are the real benefits of design thinking and where can it be applied?” The answer is that design thinking is not just a thinking method, but a powerful tool that can help you make a difference in both your work and your life.
.png)
4.1. Benefits
Effective problem solving: Design thinking provides a structured and scientific process to approach problems, helping you identify the core problem, find creative and optimal solutions, instead of just struggling with superficial symptoms.
Boosting innovation and creativity: Design thinking encourages you to break out of old ways of thinking, try new things, and create unique, groundbreaking solutions. It creates a safe environment for you to freely explore and experiment, without being afraid of “crazy” ideas.
Improve user satisfaction: Human-centered design thinking focuses on understanding and meeting real user needs. This helps you create products, services, and experiences that are truly valuable, bringing satisfaction and happiness to users.
Develop thinking skills: Design thinking not only helps you solve problems but also helps you develop important thinking skills such as critical thinking, creative thinking, problem-solving thinking, and teamwork.
4.2. Application
Design thinking is not limited to a specific field, but can be widely applied in many aspects of life, including:
.png)
In business:
Developing new products/services: Design thinking helps businesses understand customer needs, thereby creating new products and services that meet market needs.
Process Improvement: Design thinking can help businesses optimize workflows, reduce waste, and increase productivity and efficiency.
Solving internal problems: Design thinking can help businesses solve internal problems such as team conflict, lack of collaboration, or lack of motivation.
In education:
Curriculum Design: Design thinking can help educators design curriculum that meets students' needs, creating engaging and effective learning experiences.
Teaching methods: Design thinking can help teachers innovate teaching methods, enhance teacher-student interaction, and encourage student engagement in the learning process.
.png)
In social issues:
Solving community problems: Design thinking can help social organizations address problems like poverty, inequality, or lack of infrastructure.
Environmental protection: Design thinking can help find innovative solutions to protect the environment, reduce pollution, and use resources sustainably.
In personal life:
Solving everyday problems: Design thinking can help you solve everyday problems more effectively, from organizing work, planning activities, to resolving conflicts in life.
Improve relationships: Design thinking can help you better understand the needs and desires of those around you, thereby improving personal relationships and creating deeper connections.
Hopefully this article has helped you gain a clearer understanding of design thinking and inspired you to start your journey of applying it to your own work and life. Let creativity and understanding be the guiding principles in all your decisions.