Best Selling Products
What is Isometric? Applications of the isometric method in practice
Nội dung
- 1. What is Isometric?
- 2. Meaning of Isometric method
- 3. Characteristics of isometric
- 4. Uses of isometric drawings
- 5. Methods to help quickly sketch ideas
- 6. Isometric drawing construction method
- 6.1 Techniques for using support mesh
- 6.2 Technical SSR (Scale, Shear, Rotate)
- 7. Application of isometric method in practice
Isometric is an effective method that helps designers easily and quickly sketch out their ideas. So, what exactly is Isometric and what does it mean? Let's find out and explore more with SaDesign in the article below.

1. What is Isometric?
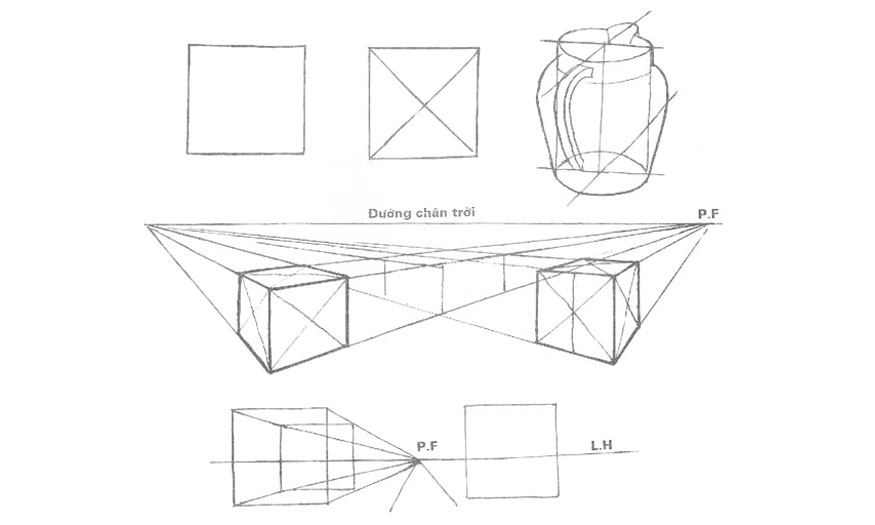
Isometric is a method used to describe the image of 3D objects in two-dimensional space. For those who are new to 3D drawing, this can be considered the most basic method.

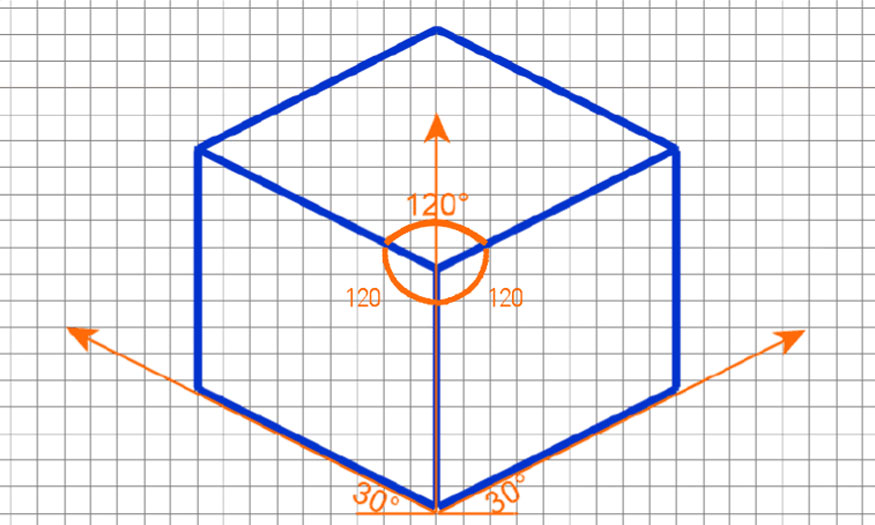
Isometric is also like an axial measurement, in which there are three coordinate axes that appear identical and the angle between any two of them is 120 degrees. All vertical lines are drawn vertically and all horizontal lines are 30 degrees off the baseline.
2. Meaning of Isometric method
Isometric drawing is important in graphics and engineering design. It helps to create 3D images on a 2D plane while maintaining the proportions and depth of the object.
The isometric drawing method will help designers easily convey their design ideas in the first stages to complete the design. After drawing the first stages, they will edit the details according to the design requirements, completing the design most completely.
Isometric will provide designers and viewers with more multi-dimensional perspectives. Specifically, it can clearly see the side and top of the design in detail, viewers will also feel more impressed and interested.
When businesses want to provide their customers with more than one option, this is a useful method to help businesses own more comprehensive and easily accessible drawings.
Isometric allows drawings to display a 3D space with microscopic or macroscopic details to increase the eye-catching and attractiveness of the design.
3. Characteristics of isometric
In isometric drawing, the x, y, and z axes are drawn at a 30-degree angle to the horizontal plane. This helps create a sense of depth without using perspective.
Details are clearly and easily recognizable, making it easy for viewers to understand the shape and structure of the object.
Use grids to ensure shapes are drawn accurately and consistently, helping to create objects with precise shapes.

Thanks to its simple structure and even proportions, this method allows designers to easily create more complex and detailed drawings. Quickly sketching out ideas as they come to mind is important for designers to focus on instead of sketching out intricate details.
4. Uses of isometric drawings
Isometric has many important uses in different fields, below we will give you more details about the application of isometric.
Thanks to isometric drawings, designers can use and organize and exchange ideas with customers, and at the same time explain to customers about assembly details.
This drawing will show the complete assembly of the parts. If you want to see the details clearly, you should use the “Exploded Isometric” drawing. This drawing will peel away the details to help you see the hidden details.
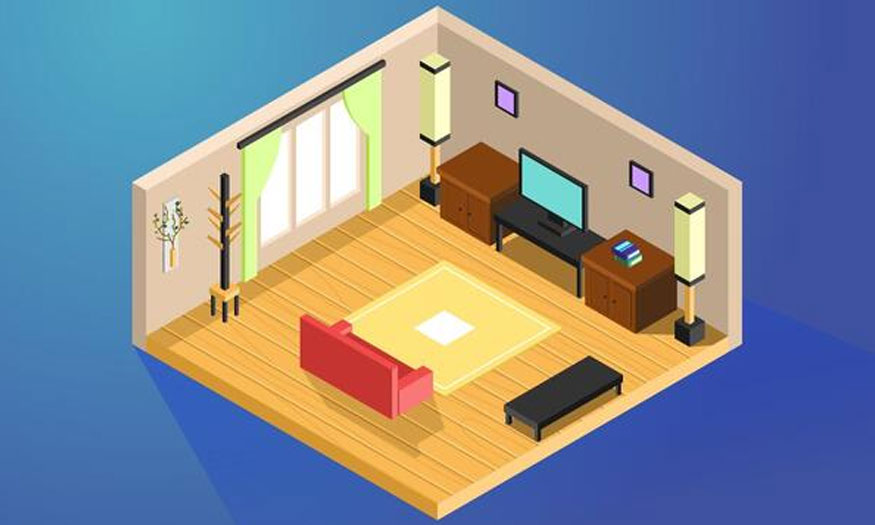

This method helps designers easily imagine 3D spaces. For those who are not specialized in this field, they can also understand the structure and details of 3D space.
In addition to supporting designers to present their ideas, these drawings also support different areas in application design, game design, software, and animation. Therefore, the Isometric method is becoming more and more useful and popular today.
5. Methods to help quickly sketch ideas
The isometric method allows the designer to focus on basic shapes without having to worry about complex perspectives. This saves time when sketching quickly.
Due to the simple and clear rules, sketching ideas using the isometric method can be done quickly while ensuring accuracy and maintaining aesthetics.
If adjustments need to be made to the idea, isometric objects can be easily changed without losing proportion or structure.
6. Isometric drawing construction method
6.1 Techniques for using support mesh
For the support grid technique, the designer needs to set up a grid system at the beginning. Then draw shapes based on that system to ensure that the shapes follow the isometric viewing rules.
To create precise guide grids, you simply combine two groups of lines: one at 30° and one at 150°.
The biggest advantage of this method is the flexibility in drawing. The guides are only for support, allowing you to freely create shapes without being limited by any rigid process. Furthermore, drawing is also very quick and simple, along the ability to adjust the size of the blocks after completion is also easy and accurate.
However, drawing on a grid system can be unsuitable for shapes that don't have square planes. For example, if you need to draw a cylinder, these guides won't be much help in creating a circle in isometric projection.
6.2 Technical SSR (Scale, Shear, Rotate)
As for SSR technique, it can be used for all different shapes. Because it can be applied to all shapes, this technique will be more complicated and have more operations.
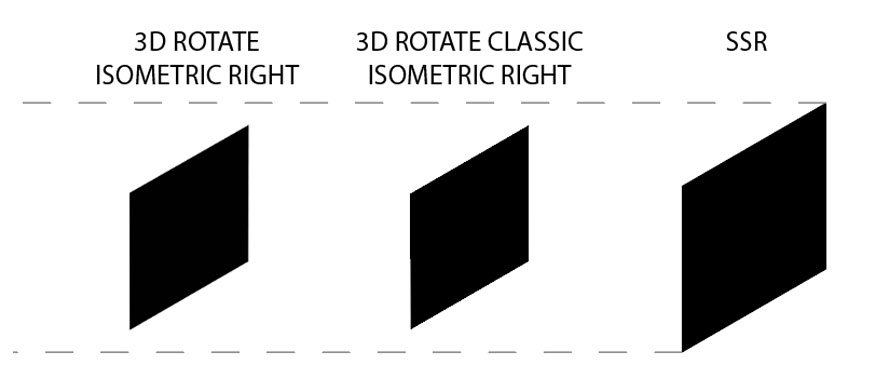
This technique requires the designer to transform a flat shape into an isometric projection. First, you need to stretch the shape vertically by about 86.062%. Next, the shape will be tilted and rotated to match the plane you want to apply it to.
Although this technique was developed primarily for Illustrator, you can do the same in other tools if needed. One advantage of this method is that it is not limited to any shape, allowing for the creation of complex shapes through SSR.
However, this process can be time-consuming and laborious, as each shape requires repeating the three steps, and for a shape with many small parts, you will have to repeat the process many times. Furthermore, if editing is required, this technique can be difficult to support the designer, as it focuses only on creating the shape and is not flexible in editing.
7. Application of isometric method in practice
Isometrics have many applications in different fields. Here are some typical applications of isometrics in practice:
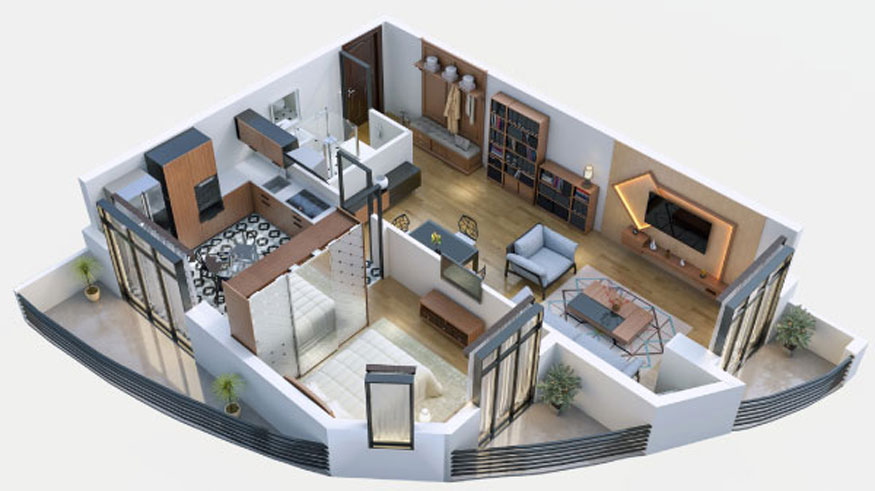

Engineers and designers use isometric drawings to represent details of machines, structures, and products, making it easier to communicate technical information.
Isometric for construction work, this is the most important drawing used for project construction because it contains all information of the pipe, list of materials, length of pipe sections, types of welds, ... helping to construct a pipeline easily and accurately.
Used to present construction designs, helping customers visualize space and structure more clearly.
Isometrics also plays a part in today's education, used in textbooks and learning materials to help students visualize geometric and spatial concepts.
Here is some basic information about the 3D Isometric drawing method for those who are considering pursuing a career in painting. If you also dream of becoming a professional designer, continue to explore more!
--------------------------------
Installation and support contact information:
🏡 SADESIGN Software Company Limited
📨 Email: phamvansa@gmail.com
🌍 Website: https://sadesign.ai