Best Selling Products
Bitmap and Vector: Understand Correctly to Design Standardly From the Start
Nội dung
Explore the difference between Bitmap and Vector images: two fundamental image formats in graphic design.
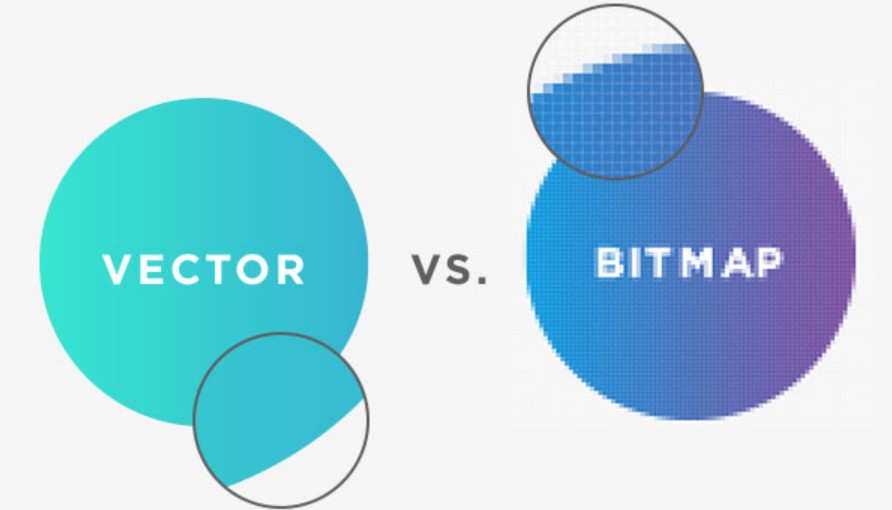
Behind every image you see on your computer screen, phone or in printed publications is a story about data structure and how that image was created. Among the popular formats, the two most frequently mentioned types of images are Bitmap and Vector .
These are two seemingly simple concepts but play an extremely important role for anyone working in the design field. Whether you are a beginner in Photoshop, learning about printing, or a professional designer, understanding the difference between Bitmap and Vector will help you avoid common mistakes such as broken images when printed in large sizes or heavy, difficult-to-handle design files.
So what is Bitmap , what is Vector and how are they different ? When should you use Bitmap images, when should you choose Vector images to achieve the best visual effect? This article will help you understand everything you need to know, from basic concepts to practical applications, so you can fully master these two important image formats.
1. What is a Bitmap Image?
Bitmap or Raster Image is a type of image created from millions of small pixels . Each pixel is shaped like a very small square containing information about its color and position in the image. When arranged next to each other, these pixels form the complete image that you see. That is why people often call Bitmap images a pixel matrix.
If you zoom in on a photo taken with a phone or digital camera in Adobe Photoshop , you’ll see tiny squares that are pixels. Each pixel contains information about color, brightness, saturation, and transparency. When you edit a photo, you’re changing the color value of each of those pixels.
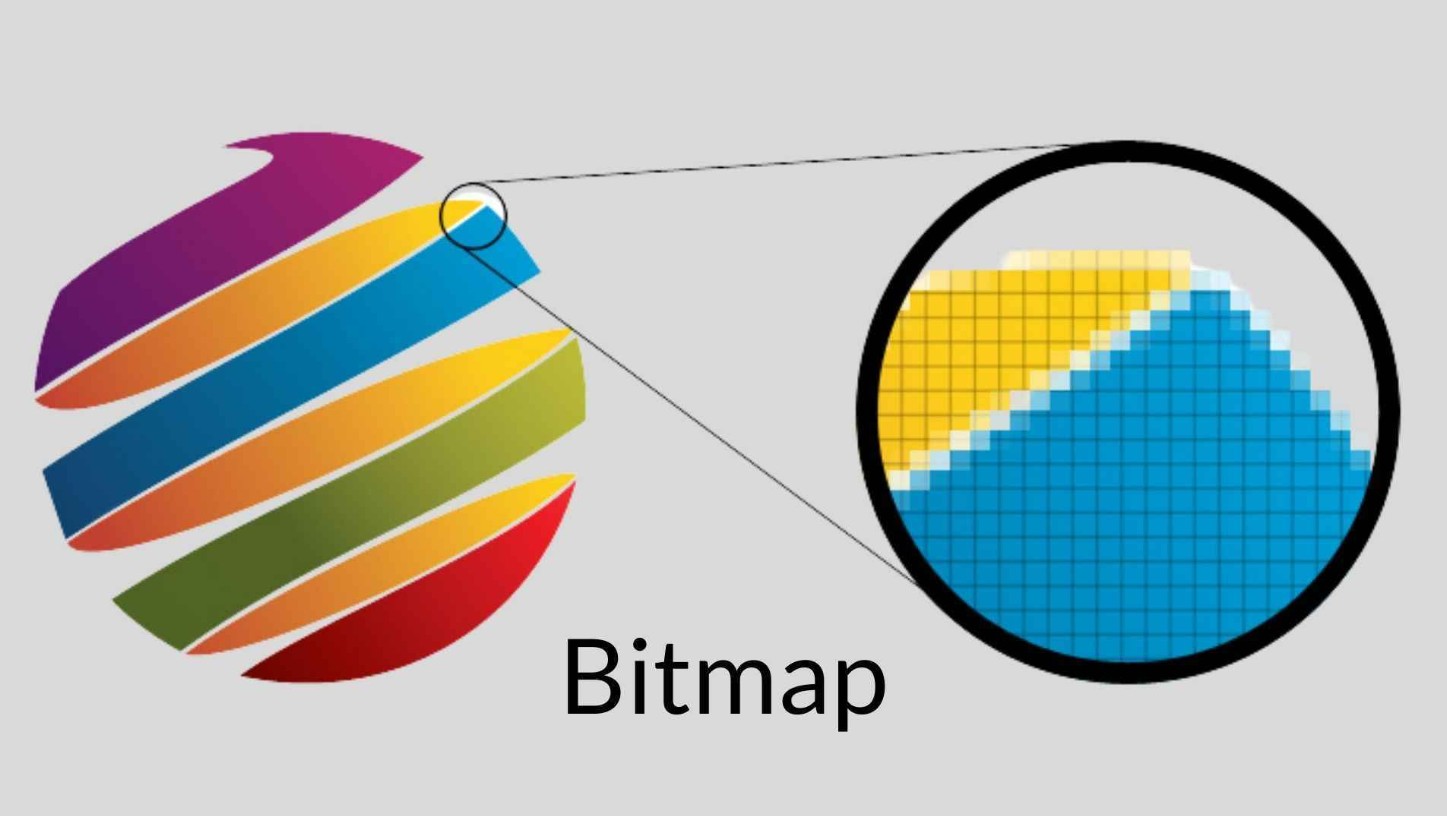
Bitmap images are widely used in fields such as photography, printing, image editing, advertising design and products that require high realism. This type of image is ideal for expressing details, light, and smooth color transitions.
An important characteristic of Bitmap images is that they are completely resolution dependent . The higher the resolution, the more pixels, the sharper the image. Conversely, when you enlarge a Bitmap image beyond its original resolution, the pixels become visible, making the image appear “jagged” or blurry.
Some popular Bitmap image formats include JPG, JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, TIFF . Of which, JPG format is often used for photos, PNG for graphic images that require transparent background, and GIF is often used for animations or simple illustrations.
In terms of editing software, Adobe Photoshop is the leading standard tool for processing Bitmap images. In addition, Corel Photo-Paint or Microsoft Paint can also be used for simple operations. Thanks to its flexibility and ability to display details, Bitmap images have almost become an indispensable foundation in modern design.
2. What is a Vector Image?
In contrast to Bitmaps, Vector images are created based on mathematical formulas instead of pixels. Each line, shape, or area of color in a Vector image is described by an equation, which includes elements such as coordinates, length, curvature, and direction.

Because of this structure, Vector images can be scaled up or down infinitely without any loss of quality. Whether you print a small logo on a business card or blow it up to the size of a billboard, the image will remain sharp and detailed.
This makes Vector images a top choice for iconic or scalable designs, such as brand logos, logos, icons, digital illustrations, or app interfaces.
Popular Vector image formats include AI (Adobe Illustrator), EPS, SVG, PDF, CDR (CorelDRAW) . These are formats compatible with specialized vector design software such as Adobe Illustrator , CorelDRAW , Inkscape or Affinity Designer .
Unlike Bitmap, Vector images are very light in size because they do not store each pixel but only remember the formula that describes the objects. When the software displays the image, it will recalculate according to that formula to draw the shape on the screen.
Another advantage of Vector images is the flexibility of editing. You can change the size, color, and shape of objects easily without affecting the overall quality of the image.

However, Vector images cannot represent complex images with many color transitions like real photos. Therefore, it is often used for graphic designs that are symbolic, simple or flat design.
3. What is the difference between Vector images and Bitmap images?
When comparing Vector images and Bitmap images, their differences are evident in three main factors: image format , image structure , and storage capacity .
In terms of image formats, Bitmap and Vector use two completely different groups of formats due to the different ways of storing data. Bitmap images usually have the extension .jpg, .jpeg, .png, .gif, .bmp, .tiff and are commonly used in photography, web design or advertising printing. Meanwhile, Vector images have the format .ai, .cdr, .eps, .svg, .pdf and often appear in professional design software such as Illustrator or CorelDRAW.
One thing that is noticeable when working with these two types of images is the ability to scale. When you open a JPG file in Illustrator, the software automatically “rasterizes” the image, that is, converts it to Bitmap format for display. Conversely, when you open an AI file in Photoshop, you will be asked to choose the size and resolution, because Photoshop cannot display Vector images without converting.
In terms of structure, Bitmap images are made up of millions of pixels, so they depend greatly on resolution. Resolution is measured in DPI (dots per inch) or PPI (pixels per inch). If you increase the size of an image without increasing the resolution accordingly, the image will be pixelated. On the contrary, Vector images do not depend on resolution but are based on mathematical formulas, so enlarging or shrinking does not affect the quality.
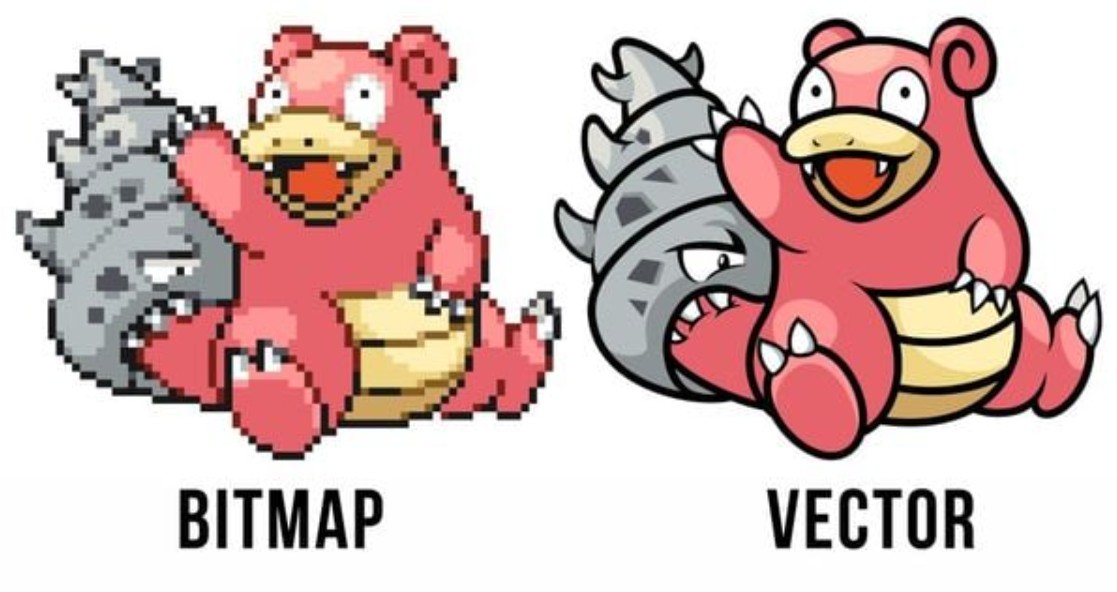

In terms of capacity, Bitmap images are often much heavier than Vector images. Because Bitmap must store data for each pixel, while Vector only needs to store the formulas of the shapes. Thanks to that, Vector images are lighter, easier to share and load faster on the web. This is also the reason why in website design, icons or logos are often created in Vector format to ensure page loading speed.
4. Advantages and disadvantages of Vector images and Bitmap images
Bitmap and Vector images both have their own advantages, depending on the intended use.
Bitmap images have outstanding advantages in displaying details and realistic colors. Landscape, portrait or advertising product photos all use Bitmap to display contrast and light naturally. Professional image processing software such as Photoshop is built to work optimally with Bitmap, allowing users to edit, color, add effects or manipulate light accurately.
However, Bitmaps have a major drawback: they depend entirely on resolution. When enlarged too much, the image will appear broken, jagged, or blurry. In addition, Bitmaps often take up a large amount of space, making it slower to store or send files over the network.
Meanwhile, Vector images have the advantage of being scalable and flexible. You can enlarge the logo hundreds of times without fear of losing sharpness. The outlines and shapes are always displayed smoothly thanks to mathematical formulas that determine their position and direction. Vectors also allow designers to easily edit every small detail such as changing colors, shapes or adding or removing elements without affecting the entire layout.

However, Vector images are not suitable when you need to express complex images or have too much detail. For example, if you want to design a portrait or landscape with subtle color transitions, Vector will have a hard time reproducing that depth and softness. In addition, Vector is limited in the number of colors and lighting effects.
5. Things to note about Vector images and Bitmap images
When working in a design environment, it is important to understand the conversion process between these two types of images. You can easily convert Vector images to Bitmap , this process is called rasterizing . When rasterizing, the software will convert the mathematical formulas of the Vector image into a matrix of pixels to display on the screen.
However, the opposite is not so simple, that is, converting Bitmap images to Vector images . Since Bitmaps only contain pixel data, the software has to “guess” the lines and shapes to create Vector images. This leads to the conversion results often being imperfect, especially with images that have too much detail.
Before converting, you should save the original Vector file to avoid losing the flexibility of editing. Once converted to Bitmap, the image will lose its infinite scalability.
Another important point is that a photo or scan cannot be converted to a Vector simply by changing the file extension . To convert it correctly, you need to use a specialized tool such as Image Trace in Illustrator or PowerTRACE in CorelDRAW . The software will automatically recognize areas of color and lines and recreate them into vector shapes.

In addition, when exporting files for printing or uploading to the web, you need to consider the purpose of use to choose the appropriate format. If you design a poster, flyer or product photo, choose Bitmap to show details. If you design a logo, icon or website interface, Vector will be the optimal choice.
6. Conclusion
Both Bitmap and Vector are two core image formats in graphic design, each with its own strengths and applications. Bitmap is the ideal choice for photos with rich details and colors, showing depth and realism. Meanwhile, Vector is an indispensable tool when you need sharp, flexible images that can be enlarged indefinitely without worrying about quality loss. Understanding the difference between these two types of images not only helps you choose the right format when designing, but also helps optimize your workflow, save space and improve the quality of the final product. If Bitmap is the "soul of photography", Vector is the "heart of brand design".












































